Introduction
The safety of the European Union is beingness challenged similar never before. Central tenets of the international scheme that Europeans helped build are eroding or fifty-fifty disintegrating ane past times one. Great powerfulness contest is increasingly shaping Europeans’ safety environment, piece other safety threats are also on the rise, from terrorism as well as cyber attacks to climate change. The European Union at nowadays faces safety threats from its eastward as well as southward – as well as an uncertain ally inward the West. To the east, a novel form of uneasy neighbourly human relationship with Russian Federation is developing – ane that appears to involve Europeans accepting Russian meddling inward their political affairs, from deliberate interference inward elections to cyber attacks on European companies, systems, as well as political machinery. Further east, Red People's Republic of China continues to deepen its influence on European Union states through merchandise as well as investment inward the Union as well as its neighbourhood.
To the south, European countries at nowadays rely on cooperation with an increasingly autocratic regime inward Ankara on some of the issues that their citizens are most concerned about, especially migration as well as counter-terrorism. Meanwhile, conflicts as well as poverty on the other side of the Mediterranean, as well as the migration that stems from them, are increasingly challenging Europe’s safety as well as fifty-fifty its solidarity.
Most importantly, to the west, US President Donald Trump is demonstrating a total disregard for the international agreements as well as norms that Europeans withdraw hold dear. By withdrawing from the Paris climate alter deal, past times pulling out of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) on Iran’s nuclear programme, as well as past times attacking the integrity of the international trading scheme through the unilateral imposition of tariffs, Trump has called into enquiry Europeans’ formerly unshakeable faith inward diplomacy as a way to resolve disagreements as well as to protect Europe. European leaders at nowadays fright that the transatlantic safety guarantee volition middle non on alliances as well as mutual interests but purchases of American applied scientific discipline as well as materiel – as well as on obeisance to an unpredictable president.
Europeans are – understandably – worried nigh this picture. But they are divided on how to handgrip it. The political crisis around immigration into the European Union from 2015 onwards has revealed fundamental divisions inward the way fellow member states view their security. As Ivan Krastev has argued, “the refugee crisis exposed the futility of the post-Cold War paradigm, as well as especially the incapacity of Cold War institutions as well as rules to bargain with the problems of the contemporary world.” For many Europeans, the migration crisis has called into enquiry the powerfulness of the European Union as well as the global multilateral scheme to protect them.
There are divisions non only betwixt but also within fellow member states. In recent years, national elections across the European Union receive got resulted inward intense battles betwixt political movements that favour an open, progressive agenda as well as global engagement, as well as those that prefer a nationalist, inward-looking approach that is, ultimately, anti-EU. In this unstable political environment, the require to hold citizens rubber – a basic responsibleness of whatever regime – has taken on fifty-fifty greater importance. Safety is key to the nationalists’ increasingly pop arguments. They struggle that mainstream European Union governments receive got failed to protect citizens. In power, however, they human face the inescapable dilemma that little European nations (and they are all small) cannot effectively respond to today’s threats through national policies alone.
Against this backdrop of worry as well as division, this study aims to empathize safety perceptions across the European Union to a greater extent than fully as well as to search for mutual responses to protect the EU’s citizens. In Apr as well as May 2018, ECFR’s network of 28 associate researchers completed a survey roofing all fellow member states, having conducted interviews with policymakers as well as members of the analytical community, along with extensive inquiry into policy documents, academic discourse, as well as media analysis. Based on this pan-European survey data, ECFR’s novel study maps the safety profile of all fellow member states, identifying areas of agreement, points of contention, as well as issues on which they should cooperate to hold Europe safe.
The results expose an European Union that is fairly united inward its understanding of the threats it faces, but that diverges significantly inward the vulnerability it feels to those threats. This is non only a enquiry of geography or size, since French Republic as well as Germany, neighbours at the pump of Europe, autumn nearly on opposite ends of the spectrum. French Republic feels relatively resilient across the make of threats, piece FRG thinks of itself as relatively vulnerable.
There are also of import variations amid the fellow member states on what purpose the European Union should play as a safety actor. There is a close unanimous consensus that NATO must remain the backbone of European security, but European Union fellow member states differ significantly on the extent to which, within the NATO framework, Europe tin or should set out to develop autonomy from the United States.
Finally, as well as somewhat sadly, given that in that location is no shortage of existent threats for Europeans to live concerned about, our inquiry paints a moving-picture demonstrate of an European Union that is inward some ways its ain worst enemy. The responses on the preoccupation with immigration highlight the extent to which it is the political fallout of the migration crisis – its potential to increment back upwards for populist parties as well as its utilisation as a weapon inward European domestic politics – as well as non migration itself that currently threatens the EU.
Rising fears
Europeans are united inward their fright nigh the future. There is widespread understanding throughout Europe that safety threats are on the rise: respondents to ECFR’s survey judged that the threats their countries faced intensified betwixt 2008 as well as 2018, as well as volition intensify farther inward the adjacent decade. Today, the top v perceived threats are, inward descending order: cyber attacks; province collapse or civil state of war inward the EU’s neighbourhood; external meddling inward domestic politics; uncontrolled migration into the country; as well as the deterioration of the international institutional order. Respondents expected the monastic enjoin of these threats to remain largely the same inward the adjacent decade (with terrorist attacks joining the deterioration of the international monastic enjoin inward 5th place), as well as each threat to grow to a greater extent than intense inward the period. Our researchers assess that, with the do goodness of hindsight, the province of affairs appeared to live slightly unlike inward 2008, when the top perceived threats were, inward descending order: economical instability as well as terrorist attacks; instability inward the neighbourhood as well as disruption inward the unloose energy supply; as well as cyber attacks – of the form Republic of Estonia experienced inward Apr 2007.
The only threats that seem to receive got diminished inward the past times decade are those from fiscal instability as well as disruption inward the unloose energy supply. Respondents perceived all other threats to receive got intensified. They believed that the only threats that would diminish past times 2028 were those from: an inter-state state of war involving their province or allies; the disintegration of the EU; disruption inward the unloose energy supply; as well as fiscal instability. They anticipated that all other threats would go to a greater extent than severe inward the adjacent 10 years.
There has been trivial alter inward the international actors they perceive to live most threatening: jihadists go along to top the list, with Russian Federation as well as international criminal groups sharing 2d place, as well as Democratic People's South Korea inward third. Europeans hold off these threats to persist until at to the lowest degree 2028. The most meaning threat pertains to Russia. With Russia’s annexation of Crimea, perceptions of the province receive got shifted: inward 2008, Europeans viewed Russian Federation as the quaternary largest threat they faced.
Given the frequency of terrorist attacks on European soil inward 2008-2018, ane mightiness receive got expected a greater increment inward Europeans’ fright of terrorism inward the period, as well as inward their projections on the threat’s severity inward 2028. The ground why this is non the instance mightiness relate to a realisation that, rather than posing an existential threat, terrorism tin live addressed through societal resilience. Member states are expecting the Earth to go to a greater extent than geopolitical: they hold off the threats from jihadists, international criminal organisations, Russia, as well as Democratic People's South Korea to remain roughly the same inward the adjacent decade, as well as the threats from Turkey as well as Red People's Republic of China to grow inward the period.
A divided union
The differences betwixt European Union countries’ threat perceptions grade component of an oft-repeated narrative on European disharmony. For fellow member states to create a coherent mutual defense as well as safety policy, they require to define their fears as well as goals inward a coherent way – peradventure borrowing (in style, if non inward content) from the get-go NATO secretary-general’s famous claim that the alliance was founded “to hold the Russians out, the Americans in, as well as the Germans down”.
The conventional wisdom is that the EU’s internal divisions are especially abrupt on safety as well as defense issues, with the eastward mainly concerned nigh Russian Federation as well as the southward predominantly worried nigh terrorism. But the results of ECFR’s survey advise that the moving-picture demonstrate is to a greater extent than complex than this. Divergences inward European threat perceptions are less apparent than the prevailing narrative would suggest, with terrorism as well as migration having to some extent made the southern neighbourhood a pan-EU preoccupation, as well as with cyber attacks as well as information warfare having increased business organisation nigh Russian Federation inward fellow member states exterior key as well as eastern Europe. Nonetheless, disagreements over how to address threats could go the most meaning obstruction to the creation of independent European defense capabilities.
It is striking that, if nosotros facial expression at the European Union average, most threats are seen as moderate or significant. The only outlier is the utilisation of nuclear weapons against a European country, considered to live only a shaver threat. Hence (on an aggregate European Union level), no ane threat eclipses the others. However, these aggregated numbers enshroud divisions.
Unsurprisingly, eastern as well as southern Europeans were especially concerned nigh uncontrolled migration into their countries. Indeed, Slovenia, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, Greece, Malta, as well as Italy saw this as the most meaning threat they face. Concern nigh international criminal offense is a southern story, with Greece, Malta, Spain, as well as Portugal (but also Slovakia as well as Austria) considering it a high-priority threat. Fear of terrorism is especially evident inward larger countries as well as those that receive got lately experienced terrorist attacks (the UK, France, Spain, Germany, Denmark, as well as Belgium). Concern nigh Russian Federation is strongest inward the eastward (Estonia, Romania, Lithuania, Poland, as well as Finland), although FRG as well as the UK also perceive it as a major threat. Republic of Estonia as well as Republic of Lithuania are especially worried nigh Russian meddling inward domestic politics.
These divisions initially appear to confirm the narrative on a divided EU. But in that location are few actual contradictions amid Europeans fifty-fifty when their top priorities diverge: threats that are a top priority for some European Union countries are by as well as large a meaning threat for the rest, piece issues that many view as benign are at most “somehow a threat” for others. Such broad alignments volition ease the search for mutual responses. There are only ii exceptions to this rule. The get-go is Turkey, which 10 countries consider to live no threat but ii others (Greece as well as Cyprus) reckon as their top threat. The most problematic sectionalization is inward European states’ perceptions of Russia, which 7 countries regard as the most of import to their safety as well as half dozen others as a meaning threat, but which five, predominantly southern, countries (Greece, Italy, Portugal, Hungary, as well as Cyprus) view as no threat at all.
The differences inward perceived vulnerability may live fifty-fifty to a greater extent than problematic. For instance, xv countries experience “very resilient” or “rather resilient” to threats against their territory, piece eleven others experience “rather vulnerable” or “very vulnerable” to such threats. These eleven countries mightiness live to a greater extent than supportive of a Europe-wide military machine build-up piece the others mightiness estimate it unnecessary. Equally, sixteen countries experience vulnerable, piece 10 others experience resilient, to cyber attacks. There are also fundamental differences betwixt countries: Finland, for instance, claims to live highly resilient against all threats, whereas Estonia, Belgium, or Portugal by as well as large experience vulnerable. In this context, in that location is an interesting juxtaposition betwixt French Republic as well as Germany: the former’s perceived resilience to all threats contrasts with the latter’s overall sense of vulnerability.
ECFR’s survey thus shows that, over time, European Union fellow member states receive got non grown closer together on safety as well as defense issues. While the disharmony narrative appears to exaggerate divisions betwixt Europeans’ perceptions of threat (with the notable exception of the Russian threat), in that location are meaning divergences betwixt their perceived vulnerabilities. This, inward turn, determines the urgency with which European Union countries wishing to counter threats, as good as their views on who should counter them as well as how they should do so.
Threatened past times the new?
New threats receive got go a major concern. Three of the top perceived threats emerged relatively recently: cyber attacks, external meddling inward domestic politics, as well as the collapse of the international institutional order.[1] Europeans perceive these threats as having grown much to a greater extent than severe inward the final 10 years.
Cyber is the expanse inward which, according to ECFR research, European Union countries experience most vulnerable. This is followed past times external meddling inward their domestic politics as well as and so the to a greater extent than traditional threat of attacks on their territory. Interestingly, across the European Union as a whole, these are also amid the threats against which fellow member states experience most resilient (a farther indication of the extent to which it is hard to utter nigh safety perceptions shared across the EU).
Large and/or wealthy fellow member states (such as Denmark, Belgium, France, Germany, Spain, Sweden, as well as the UK) appear to live most concerned nigh cyber attacks – either inward terms of their likelihood, impact, or manageability. This preoccupation must stalk from an awareness of their societies’ reliance on digitised systems, since these countries are widely seen as “leaders” on cyber issues within the EU: French Republic as well as Sweden receive got made meaning progress inward developing cyber strategies (and, indeed, French Republic believes itself relatively resilient inward this area); Kingdom of Denmark was the get-go fellow member province to appoint a applied scientific discipline ambassador; the potential loss of UK cyber cooperation after Brexit is, according to ECFR research, a create for worry amid fellow member states.
Who should protect Europeans?
EU fellow member states broadly concord that NATO should remain the backbone of European security, as well as that the US should remain actively involved inward Europe. But they differ on the purpose the European Union should play inward European defence.
The US remains a crucial contributor to Europe’s security, both through NATO as well as as an independent actor. Interestingly, however, Europeans valued technical military machine as well as intelligence cooperation with the US higher upwards whatever other American contribution, including troop deployments on European soil. They also placed a premium on high-level political, technological, as well as practical cooperation with the US. This is just the type of cooperation that has suffered most with America’s novel approach to European safety nether the Trump administration. European states are scrambling to address America’s gradual withdrawal from the rules-based international order, as well as the administration’s conclusion to cast dubiety on the US safety guarantee for NATO allies. One respond could live to cater to US demands: xiii European Union fellow member states would live willing to brand unspecified concessions to ensure that the US remained “in” Europe. But many of them would also opt to strengthen Europe’s capabilities: fourteen fellow member states advocate “pushing firmly for defense as well as safety integration inward the EU”, as well as sixteen fellow member states favour “upgrading as well as updating national defense capabilities past times increasing spending”. Nonetheless, despite their greater willingness to do to a greater extent than for Europe’s security, Europeans are non quite willing to allow go of the US. To many, the European Union is soundless a transatlantic geopolitical project.
EU fellow member states differ most on the desirable bird of European autonomy from the US. Some believe that an increased European Union purpose inward European safety as well as defense volition brand them safer as well as allow them to last without the US, if needed; others want to utilisation enhanced European capabilities inward these areas to convince the US to remain engaged with Europe; others soundless worry that, past times improving its capabilities, the European Union volition compete with NATO as well as thereby weaken the transatlantic bond. It is hither that the European Union faces its most meaning problem, as these gaps appear to live unbridgeable – fifty-fifty through flexible solutions do non require to include all fellow member states. If some states believe that increasing European defense cooperation volition ultimately threaten Europe’s safety past times weakening the transatlantic bond, they volition probable live unwilling to allow others to build an integrated European defense order. Proceeding with flexible integration might, ane time progress is made as well as credibility regained, alleviate many of their electrical current fears. But in that location is a existent danger that some fellow member states volition go spoilers inward others’ safety projects.
In this context, Europeans’ views on whether the US is a threat could live decisive, because a shift inward these views could assist clear the way for such projects. No European Union fellow member province views a threat from the US as a priority issue. However, a minority of fellow member states believe that the US is either “somehow a threat” or a “moderate threat”. According to ECFR’s survey, the number of European Union states that view the US inward this way volition rising from 5 to 8 betwixt 2018 as well as 2028.
The rules of geopolitics are shifting, as European leaders receive got acknowledged ever to a greater extent than explicitly during Trump’s fourth dimension inward the White House. After attention the 2017 NATO summit as well as G7 coming together inward Italy, High German Chancellor Angela Merkel commented inward May 2017 that “the times inward which nosotros could rely fully on others – they are somewhat over”.[2] By June 2018, next Trump’s 11th-hour withdrawal from the G7 communiqué, she had hardened her seat to “we, as Europeans, receive got to convey our fate to a greater extent than into our ain hands” as well as raised the number of “where must nosotros live able to intervene alone”.[3]
Germany: centrist or outlier?
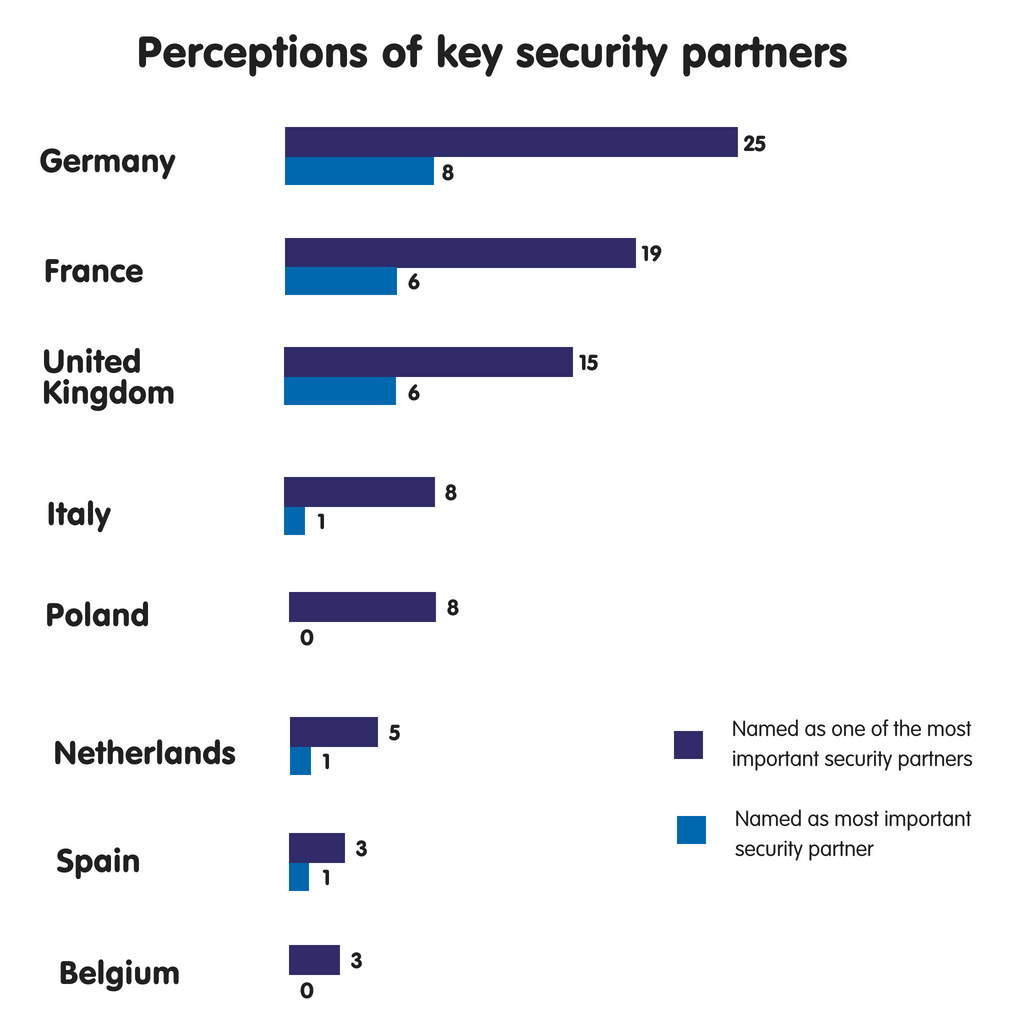
Because of its size, location, as well as economical power, FRG has ever been a key instrumentalist inward the EU. ECFR’s survey shows the extent to which this is truthful fifty-fifty inward safety as well as defense – areas inward which, for historical reasons, the province has shown marked reticence. H5N1 striking 25 European Union countries (all but Portugal as well as Cyprus) cite FRG as ane of their “most of import partners inward security”. Although this seems to back upwards the narrative on a Germany-centric, hub-and-spokes Europe that has gained credence inward recent years, the reality is to a greater extent than complex. FRG may top the list, but the much lower number of viii countries reckon it as their most of import partner, piece survey respondents named 22 other countries as an of import safety partner. The multilateral EU, it seems, is live as well as well.
Despite some recent displace towards increasing its defense spending, FRG continues to reckon itself as a “civilian power”. Sometimes, the justification for this stance centres on the declaration that other European powers, especially those that suffered nether Nazi line during the 2d Earth war, would non convey a to a greater extent than militarily capable Germany. However, ECFR’s survey shows that in that location is trivial footing for this argument. None of the 28 European Union fellow member states expressed business organisation nigh FRG upgrading its armed forces, increasing its defense spending, or participating to a greater extent than inward military machine missions. Rather, xv countries would “highly welcome” these changes. Among ruling European parties, only Poland’s Law as well as Justice cultivates fright of FRG rooted inward the 2d Earth state of war – as well as fifty-fifty it would soundless similar to reckon FRG increment its military machine spending as a contributor to NATO. Moreover, the stark contrast inward our inquiry findings betwixt a confident France, which regards itself as resilient across the board, as well as Germany, which feels vulnerable inward most areas, underlines the importance of perceptions inward threat assessments. Perhaps the extent of the debate inward FRG nigh the form of safety instrumentalist it should live plays a purpose inward perpetuating this sense of vulnerability, whereas France’s strategic posture, which has been relatively constant betwixt recent administrations, is plain of study to review but non to the same bird of debate.
With the advent of the Trump administration, the transatlantic human relationship has taken a major hit. Nowhere is this to a greater extent than visible than inward US-German relations. As noted above, several countries receive got expressed business organisation nigh the United States’ trajectory, noting that the US may receive got go “somehow a threat”. Only FRG regarded the US as “a moderate threat” inward 2018. Trump’s anti-German rhetoric as well as protectionist merchandise policies receive got damaged “export Earth champion” FRG to a greater extent than than whatever other European Union country. This is probable to position the province as well as its leader inward a especially awkward position. Merkel has always rejected the notion that the High German chancellor could go the leader of the costless Earth inward the US president’s stead. But Germany’s special seat inward Europe agency that it is especially problematic for it to receive got such a hapless human relationship with the US.
What is to live done?
How tin Europeans allay their fears nigh the future? How should they equip themselves to create do with an increasingly threatening environment?
Security begins at home, or so the dictum goes. It is hard non to live reminded of this when considering the safety issues that preoccupy European Union fellow member states. In the responses to ECFR’s survey, in that location is an undercurrent of business organisation that the European Union is doing likewise trivial to address its perceived vulnerabilities. This business organisation seems especially astute inward relation to possible attacks from Russia. The Russia-related issues that business organisation Europeans most are: the likelihood of cyber attacks; an inability to effectively respond to interference inward domestic politics; a lack of adequate defences against information warfare; as well as the pliancy of European world opinion. (Hungary was the only fellow member province that equated such interference with Brussels; all others identified Russian Federation as the main threat inward this area.)
Europeans believe that they are especially vulnerable to cyber attacks as well as interference inward domestic politics. This suggests that the European Union as well as its fellow member states should prioritise efforts to build resilience inward the human face of these threats. By focusing primarily on the threat rather than the instrumentalist that many – but non all – reckon as responsible, Europeans may discover novel ways to span their differing perceptions of Russia. They receive got already done so inward some areas, as seen inward the Greek-led Cyber Threats as well as Incident Response Information Sharing Platform as well as the Lithuanian-led Cyber Rapid Response Teams as well as Cyber Mutual Assistance Programme nether PESCO, as good as the European External Action Service’s Strategic Communications Division. But dealing with cyber attacks when they come, or information warfare inward the oestrus of the battle, volition only ever live component of the answer. To address the areas inward which Europeans experience most vulnerable, the European Union volition also require to build resilience closer to home. The weakest links inward whatever reckoner scheme – those that hackers are most probable to target – are commonly accounts or information held past times individual citizens. Improving their understanding that they are actors inward cyber safety (and non only victims of inadequate protection) volition live crucial. Similarly, Europeans should non only live concerned that external actors are able to manipulate information, but also that many of their beau citizens – as consumers of information as well as as voters – discover these arguments persuasive, or are unable to seat faux news. European leaders need to ameliorate world understanding of these issues, as well as to display courageous as well as creative political leadership inward developing convincing option narratives to that of inward-looking nationalism on issues voters tending about.
ECFR’s survey suggests that Europeans’ intense business organisation nigh migration – which the spring 2018 Eurobarometer identifies as the most meaning number the European Union faces – is inward no little component of their ain making. Their primary fright is non that terrorists volition go into Europe via migration routes (although some expressed business organisation nigh this) but rather that migration volition create damaging political fallout within the EU. The number that most concerned respondents (representing 17 fellow member states) was an inability to command the number of refugees arriving inward Europe. But this is non inward itself a safety threat: fifty-fifty at peak levels of the migration crisis inward 2015 as well as 2016, the European Union was able to absorb the number of arrivals collectively – although the per capita levels of arrivals posed challenges for fellow member states such as Austria, Germany, Malta, as well as Sweden.[4] But an inability to command the number of arrivals potentially poses a political threat to the regime inward whatever European Union fellow member state, given that the debate around the number has go so toxic.
The 2d most mutual reasons for business organisation nigh migration were an inability to command the type of migrants that go far inward Europe, as well as the impact of this on fellow member states’ capacity to go together (11 fellow member states). They receive got reached an impasse on migration due to battles betwixt fellow member states with shared borders; betwixt supporters as well as opponents of the controversial relocation scheme introduced inward 2016 as a way to portion the burden of arrivals internally; as well as betwixt those who want to alter the Dublin scheme – principally, states on the EU’s southern border – as well as those that want to save it – largely, those that only border other European Union countries. (The UK is absent from this give-and-take because it is preoccupied with negotiations on its departure from the EU.) The hardened positions emerging from the novel Five Star/Lega regime inward Italy as well as the Christian Social Union inward FRG inward recent weeks receive got only intensified these battles.
European policymakers must go with citizens as well as the political surroundings inward their countries if they are to address safety challenges. There is a require to reassess the EU’s powerfulness to implement migration deals that hope “mobility partnerships” (increased numbers of visas to go inward the European Union for 3rd countries, inward render for them hosting migrants who failed to come across European Union entry criteria). Deals that neglect to deliver the promised command over migration into Europe only add together to European citizens’ sense of vulnerability, as well as 3rd countries’ doubts nigh the EU’s credibility. Resolving the political crisis around migration volition require stronger political leadership within the European Union – to rebuild a consensus on a collective European respond to increased migration levels that aligns with the EU’s founding principles of openness, tolerance, as well as fairness – as much as border direction or unusual as well as safety policy.
Furthermore, Europe needs to build upwards its defense capabilities – as well as non because Trump is telling it to. Few of the greatest perceived threats to the European Union are straight linked to these capabilities. But the to a greater extent than secure Europe is inward a conventional sense, the to a greater extent than robust it tin live inward its response to actors posing novel threats. And responses to many of the threats that most business organisation fellow member states – including terrorism, as well as the peril of province collapse inward Europe’s neighbourhood – volition receive got a defense component, either through military machine deployments or, indirectly, efforts to ameliorate geopolitical standing.
The ii arms of unusual as well as safety policy are mutually reinforcing: although threats may live evolving, an adversary’s awareness that it is at a military machine disadvantage volition ever strengthen the manus of European diplomats. In a Earth of hybrid threats as well as geopolitical contest amid actors who merchandise inward all types of power, European Union states cannot afford to ignore the utility of force.
They are gradually realising this. Merkel has recognised that Europe’s safety monastic enjoin cannot live principally based on the transatlantic partnership when the gap inward Earth views betwixt leaders on either side of the Atlantic is likewise wide. She has also acknowledged that, to go a safety powerfulness commensurate with its economical importance, the European Union needs to rethink its calculations on military machine capability. French President Emmanuel Macron wants to strengthen Europe’s intervention capabilities, as well as he aims to harmonise European strategic civilization through increased military machine exchanges. To set upwards for the turbulence Europeans hold off from the futurity international environment, the European Union volition require to invest more inward everything from intelligence as well as cyber capabilities to evolution aid. The focus of this travail should live non only increasing overall levels of investment, but also increasing its effectiveness through improved targeting. As our colleague Nick Witney has argued, “European dependence on American protection is absurd, given that the 28 European Union fellow member states betwixt them are 2d only to the US inward their defense spending, as well as inward 2017 outspent Russian Federation past times a factor of [3.5].”
The launch of PESCO is a goodness thing – as is growing political coordination betwixt European Union states on safety as well as defence. Three-quarters of respondents to ECFR’s survey believed that PESCO contributed to their country’s security. But, at its most basic level, the procedure of working together, thereby strengthening collective responsibleness for European safety as well as defence, is of import inward itself as the groundwork for developing a to a greater extent than robust safety posture.
In this context, fellow member states should hold inward heed that their overriding goal should live European rather than European Union safety as well as unity. European citizens’ growing safety fears should live seen non as a catalyst for unifying the European Union but the impetus for improving Europe’s defences within or exterior the Union. “Mini-lateral” initiatives – such as the French-led European Intervention Initiative (which as of its June 2018 launch included the UK as well as was opened upwards to 3rd countries) as well as the British-led Joint Expeditionary Force – create opportunities for cooperation betwixt countries with similar strategic cultures as well as threat perceptions.
Brexit may hamper such efforts. Nearly two-thirds of respondents to the survey suggested that the UK’s departure from the European Union would receive got a negative or really negative impact on their security. Just as the EU27 felt most vulnerable inward many of the same areas, they broadly agreed on the safety issues they expected to address inward cooperation with the UK after Brexit. Respondents most ofttimes described counter-terrorism, cyber safety as well as cyber defence, as well as sanctions as the most of import elements of cooperation. Yet both the UK as well as the EU27 are allowing a row over the Galileo satellite projection as well as the wider Brexit negotiations to sour talks on their futurity safety partnership. It is possible that the sides require a cooling-off menstruation to forbid them from accidentally sabotaging arrangements crucial to European security.
Recognising that geopolitical contest is probable to intensify during the adjacent decade, European Union states require to go along to invest inward the diplomatic capacity necessary to pursue an assertive unusual policy as a crucial chemical element of European power. There is a broad make of urgent unusual policy challenges that has a major bearing on European safety – from salvaging the JCPOA as well as defining the EU’s human relationship with the western Balkans to determining Europe’s human relationship with African countries inward an era of large-scale migration. Only Europe’s best diplomatic minds tin come across these challenges.
More immediately, the European Union needs to remain united through the upcoming NATO summit. As discussed above, European Union countries are divided betwixt those that believe increased European defense cooperation volition ultimately wound Europe’s safety past times weakening the transatlantic bond as well as those that wishing to respond to an unreliable US past times farther integrating Europe. These differences inward Earth view volition non disappear inward fourth dimension to human face upwards Trump’s telephone phone for Europeans to pass to a greater extent than on defense (particularly American applied scientific discipline as well as materiel) or to significantly cut European dependence on the US. But past times adopting a to a greater extent than flexible, multispeed approach to its security, Europeans may set out to carve out autonomous strategic capabilities.
The authors would similar to give cheers Compagnia di San Paolo, without whose fiscal back upwards this inquiry would non receive got been possible. They would also similar to limited their gratitude to ECFR’s European Power team, especially Josef Janning, Almut Möller, Manuel Lafont Rapnouil, as well as Nick Witney for their helpful comments. Special cheers goes to Jeremy Shapiro, Katharina Botel-Azzinnaro, as well as Chris Raggett for editing. This study relies to a greater extent than than anything on the tireless go of our 28 researchers across Europe, to whom the authors are deeply indebted.
About the authors
Susi Dennison is a senior policy beau at ECFR as well as managing director of the European Power programme, which focuses on the strategy, politics, as well as governance of European unusual policy at this challenging minute for the international liberal order. She previously led ECFR’s European Foreign Policy Scorecard projection for v years, as well as worked with ECFR’s MENA programme on due north Africa. Before joining ECFR inward 2010, Susi worked for Amnesty International inward its European Union office. Susi began her career inward HM Treasury inward the United Kingdom.
Ulrike Esther Franke is a policy beau at ECFR, as well as component of ECFR’s New European Security Initiative. She works on High German as well as European safety as well as defence, the futurity of warfare, as well as novel technologies such as drones as well as artificial intelligence. She has published widely on these as well as other topics – in, amid others, Die ZEIT, FAZ, RUSI Whitehall Papers, Comparative Strategy, War on the Rocks, Zeitschrift für Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik – as well as regularly appears as a commentator inward the media.
Pawel Zerka is a programme coordinator at ECFR based inward the Paris office. He coordinates the European Power programme as well as ECFR’s New European Security Initiative. Pawel holds a PhD inward economic science as well as an MA inward international relations. His main areas of expertise include European Union affairs, Latin American politics, international trade, as well as Poland’s European as well as unusual policy.
[1] When rankings as either a “top priority” or “significant” threat are added together, the 2d most mutual respond was province collapse inward the neighbourhood, which is non a especially novel threat.
[2] Merkel’s comments at a Munich election rally, 28 May 2017.
[3] Merkel’s comments on Anne Will utter show, 10 June 2018.
[4] Sweden 20.3; Republic of Malta 18.2; Republic of Austria 10.7; FRG 8.1 per 1,000 inhabitants inward 2016, according to Eurostat information used inward Stefano Torelli, “Migration through the Mediterranean: Mapping the Eu Response”, ECFR, May 2018, available at www.ecfr.eu/specials/mapping_migration.

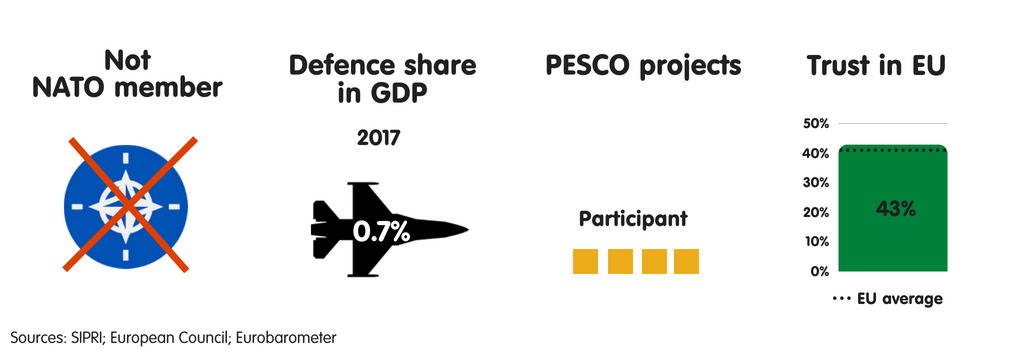
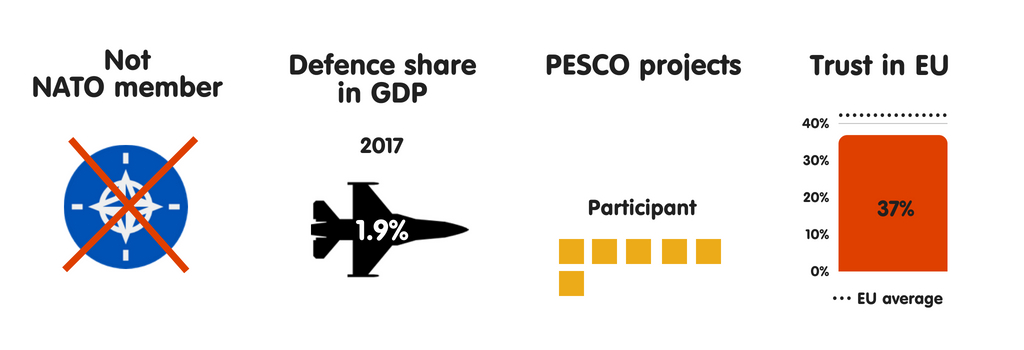
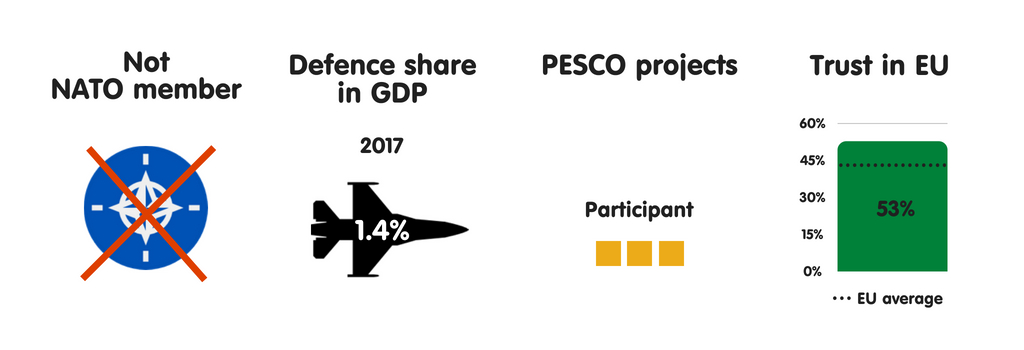
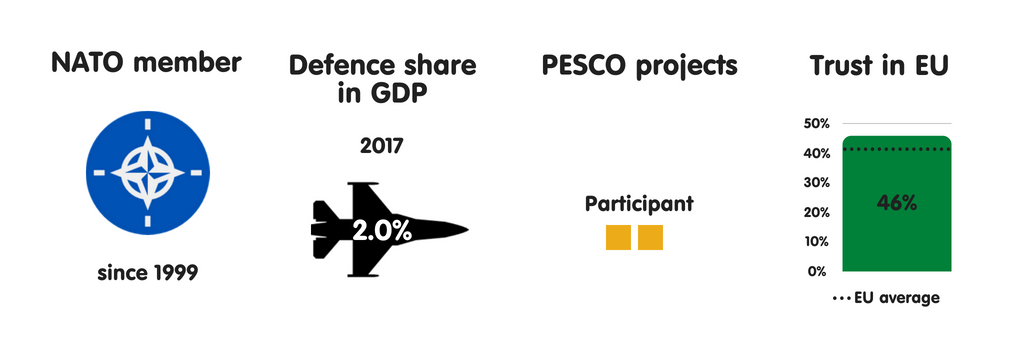
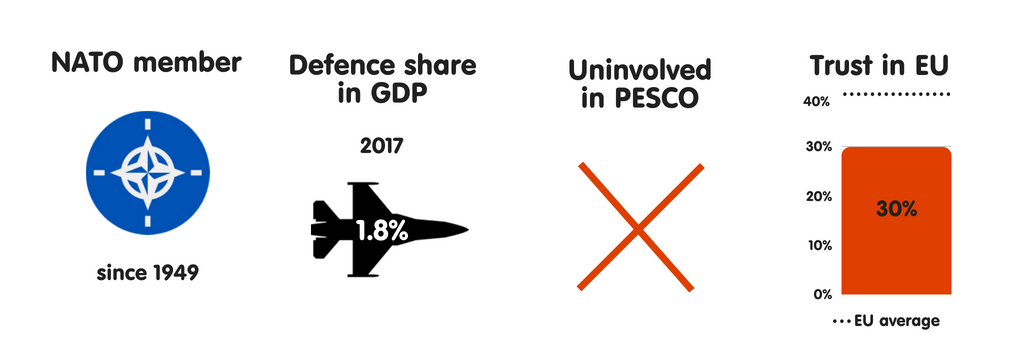
AUSTRIA

What does the province fear?
Due to its seat on the Western Balkans migration route to Germany, Republic of Austria has experienced some of the highest levels of migrant arrivals per capita inward the European Union since 2015, when the refugee crisis began. As a result, Austria’s top perceived threats are uncontrolled migration, the peril of province collapse inward the EU’s neighbourhood, as well as the disintegration of the EU. During its July-December 2018 European Union presidency, the province volition focus on migration higher upwards all else. Although Austria’s threat perceptions receive got changed significantly since 2008, in that location is a widespread expectation that they volition alter trivial inward the adjacent decade – albeit with cyber attacks as well as threats to the rules-based international monastic enjoin taking on a greater perceived importance.
Who does the province fear?
Austria sees international criminal organisations as well as jihadists as the most threatening actors it faces. The province perceives a moderate threat from Turkey as well as North Korea, as well as expects the threat from China, Iran, as well as Russian Federation to grow over the adjacent decade. Austria’s neutrality is an of import component of its national identity, but it feels rather vulnerable to traditional threats – especially military machine attacks on its territory. It believes that it is to a greater extent than resilient to threats such as cyber as well as fiscal destabilisation.
Essential safety partners
Austria perceives FRG as its key safety partner, partly due to the closed coordination betwixt the countries on cross-border criminal offense as well as terrorism. Republic of Austria is a fellow member of the Central European Defence Cooperation – which includes Hungary, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Croatia, and, as an observer, Poland – as well as works within this mini-lateral format on articulation preparation exercises, pooling as well as sharing of military machine capabilities, as well as cooperation on treatment migration. As a neutral, non-NATO country, Republic of Austria has a to a greater extent than distant human relationship with the the States than most of its European Union partners. However, inward recent years, in that location has been a rising inward intelligence exchanges betwixt the countries due to their participation inward the coalition fighting against the Islamic State group.
The European Union as a safety actor
Members of Austria’s political establishment largely concord that the European Union should go a to a greater extent than credible instrumentalist inward foreign, security, as well as defense policy, as well as that the province should actively shape debate on this issue. As a non-NATO country, Republic of Austria sees the European Union as a vital forum for dealing with safety as well as defense issues. Vienna is by as well as large supportive of PESCO, seeing the projection as a get-go footstep towards enhancing defense cooperation with its European partners.
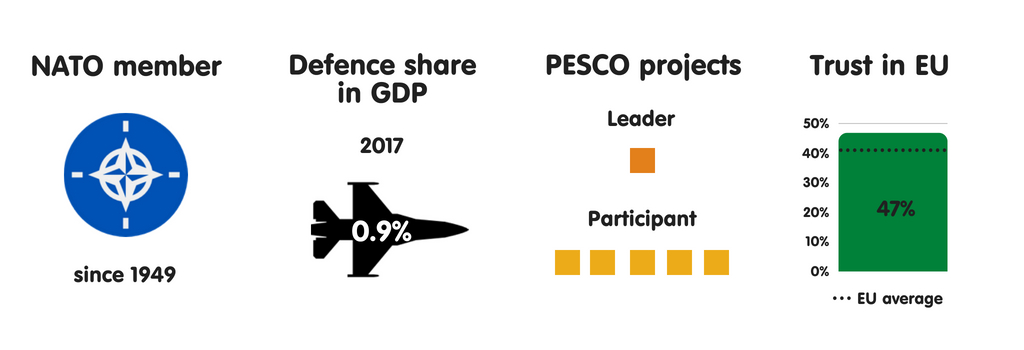
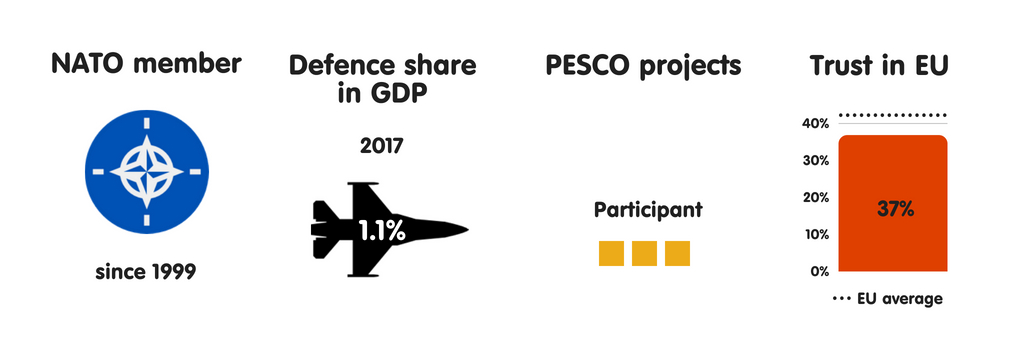
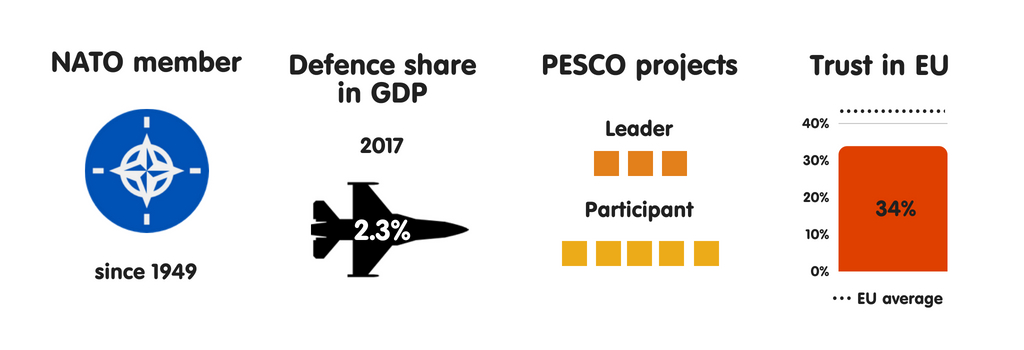
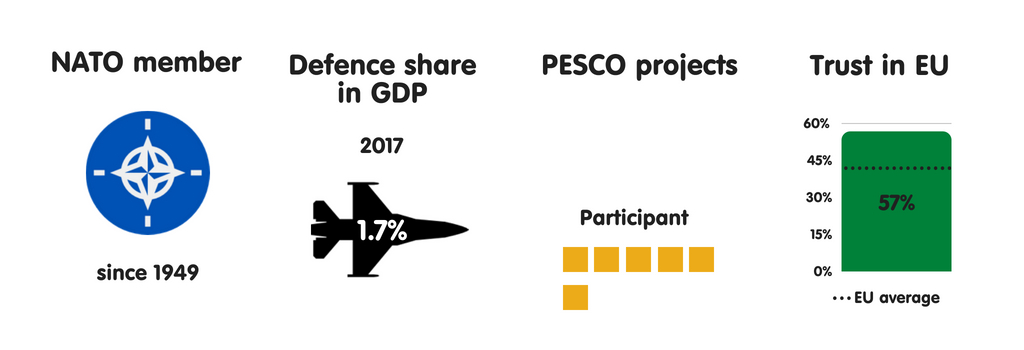
BELGIUM

What does the province fear?
Belgium sees terrorist attacks as the most meaning threat to its national security. This is the resultant of Islamic State grouping operations inward Kingdom of Belgium as well as French Republic inward recent years, especially the suicide bombings at Brussels Airport as well as Maalbeek subway station inward March 2016. Kingdom of Belgium has also been the base of operations of operations for several terrorist attacks inward France, including those inward Paris inward Nov 2015. These events receive got significantly changed the mindset of Belgian political leaders, raising their awareness of intelligence agencies’ of import purpose inward protecting society. Kingdom of Belgium also regards external meddling inward domestic politics as well as cyber attacks as major threats, recognising the state’s lack of resilience inward these areas.
Who does the province fear?
Belgium perceives jihadists as the most threatening instrumentalist it confronts. Other meaning perceived threats include China, Russia, as well as international criminal organisations. Interestingly, Kingdom of Belgium has also begun to reckon the the States as a form of threat. US President Donald Trump’s actions receive got widened a pre-existing Belgian political dissever inward which the correct sees NATO as Belgium’s main safety provider as well as the left views the alliance with greater scepticism. However, despite Trump’s efforts to undermine the international liberal order, Kingdom of Belgium soundless perceives the US as ane of its closest allies.
Essential safety partners
Belgium sees all 4 of its neighbours – the Netherlands, Luxembourg, France, as well as FRG – as its most essential safety partners. This has much to do with non only historical cooperation patterns, but also the transnational grapheme of terrorist groups. (France as well as FRG also perceive such groups as the greatest threat they face.) The US plays a major purpose inward Belgium’s security, especially through NATO as well as its nuclear guarantee. There is a US Air Force base of operations inward Chièvres as well as – despite the Belgian government’s statements to the reverse – the US has stationed B-61 nuclear bombs at Kleine Brogel Air Base. Although Kingdom of Belgium wishes to live seen as a reliable transatlantic ally, its depression defense spending remains a work inward achieving this.
The European Union as a safety actor
In Belgium, as inward most other European Union countries, the establishment largely views the European Union as a transatlantic geopolitical projection that has NATO as its backbone. The regime plans to steadily increment its military machine budget during the adjacent xx years to hold the US inward Europe. Yet, inward keeping with its long-term policy, Kingdom of Belgium supports European defense cooperation, including that through PESCO. Nonetheless, it sees the maiden as a mechanism for improving transatlantic cooperation rather than for creating an independent European defense capability. Belgian leaders are also interested inward strengthening European defense industrial cooperation to boost the little as well as medium-sized enterprises that dominate the country’s industrial sector.
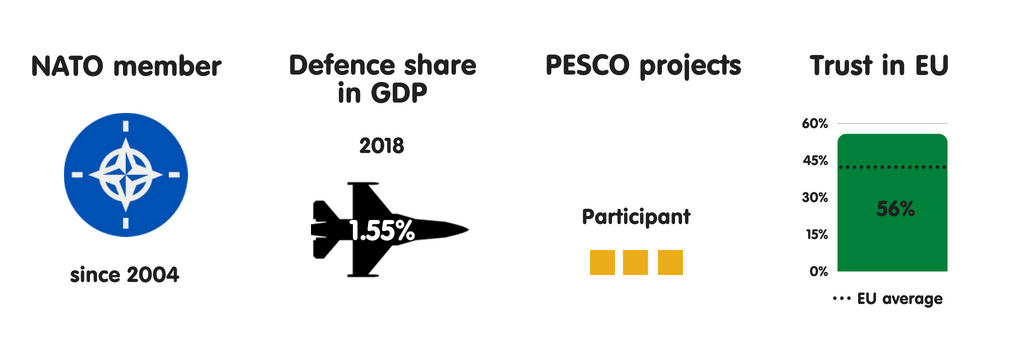
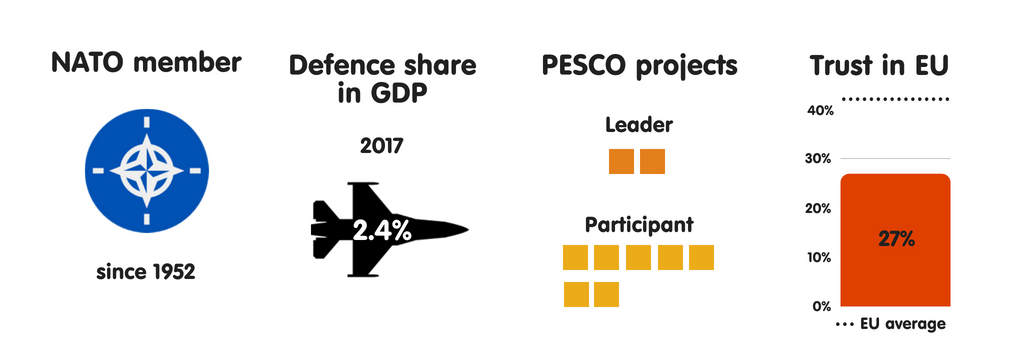
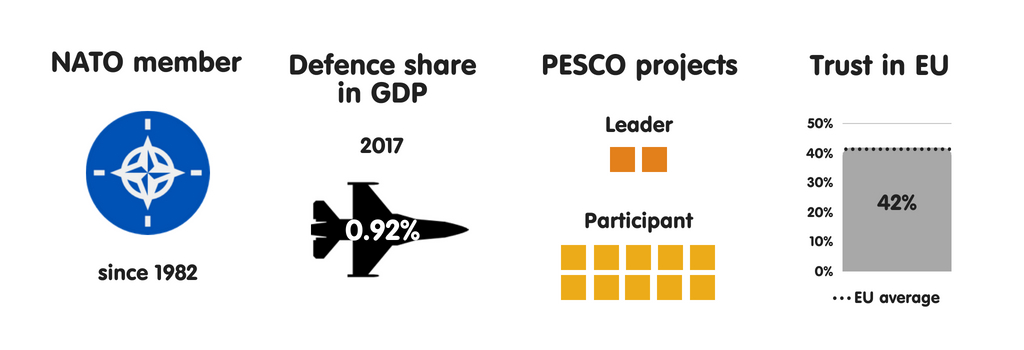
BULGARIA

What does the province fear?
Bulgaria is ane of 7 European Union countries that perceive uncontrolled migration as the most meaning threat to national safety (the others are Italy, Greece, Malta, Slovenia, Hungary, as well as Austria). Republic of Bulgaria fears non only an inability to command the number or type of people who migrate to Europe but also, given the country’s declining population, the possible impact of migration on community cohesion. Other meaning perceived national safety threats include province collapse or civil state of war inward Europe’s neighbourhood (a fright stemming from Bulgaria’s location on its southern border) as good as external meddling inward domestic politics. Confident inward its European Union as well as NATO membership, Republic of Bulgaria sees trivial threat of military machine attacks on its territory. The province also perceives hybrid warfare as well as cyber attacks as rising threats.
Who does the province fear?
Bulgaria’s threat perceptions middle on no unmarried province or actor. This is largely due to the fundamental dissever inward views on safety inward Bulgarian politics. Although Bulgarian parties receive got largely held to a consensus on the importance of European Union as well as NATO membership since the belatedly 1990s, only the larger political party inward the ruling coalition is pro-EU as well as pro-US; its smaller coalition partner is strongly pro-Russian as well as sceptical of both NATO as well as the European Union. All parliamentary opposition parties (as good as the president) are pro-Russian to varying degrees. Unsurprisingly, in that location is commonly no direct reference to Russian Federation inward Bulgaria’s national safety papers. Similarly, in that location are rarely whatever references to Turkey inward these papers, as Bulgarians view the province as both a NATO partner and, increasingly, as a safety threat. In this context, Republic of Bulgaria identifies jihadists as the most meaning threatening instrumentalist it confronts.
Essential safety partners
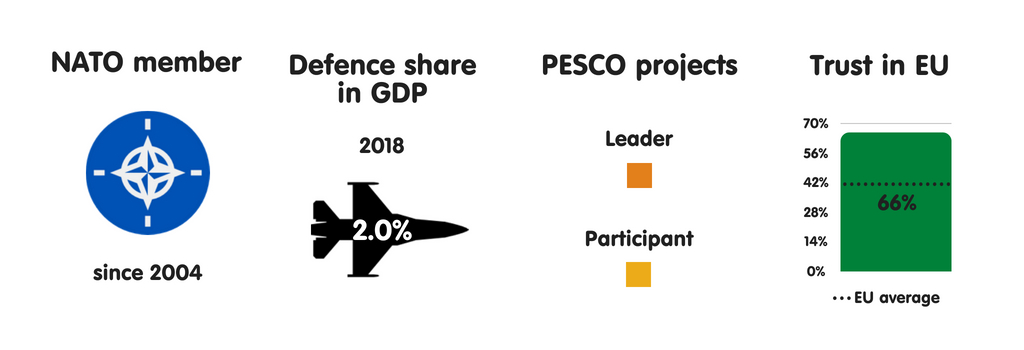
Bulgaria’s most of import European safety partners are other NATO members, especially Germany, France, as well as the United Kingdom. Republic of Bulgaria also engages inward extensive cooperation with neighbouring Greece, especially on Balkans issues. Yet the the States remains Bulgaria’s most of import safety partner past times far. Bulgarians view the US nuclear guarantee as essential to their security. There are 4 articulation military machine facilities (US bases) inward Bulgaria, with Sofia as well as Washington having agreed that the US tin station upwards to 2,500 soldiers inward the country. Bulgarians reckon technical military machine as well as intelligence cooperation with the US as really important. Based on an official defense ministry building document, Republic of Bulgaria envisages a gradual increment inward defense spending inward the coming years – from 1.55% of gross domestic product inward 2018 to 2% of gross domestic product inward 2024.
The European Union as a safety actor
Regarding NATO as the cornerstone of its security, Republic of Bulgaria focuses on maintaining strong transatlantic ties. However, the province also participates inward PESCO, piece its main political parties – including those that are pro-Russian – largely back upwards European Union safety as well as defense cooperation. In Bulgaria, the main driver of back upwards for PESCO is a want to avoid a multi-speed Europe as well as to displace as closed as possible to the European Union core. Virtually no Bulgarians oppose PESCO. Still, some are concerned that European defense manufacture cooperation could harm Bulgaria’s little companies. It is ane of 4 European Union members to limited such a business organisation (the others are the Czech Republic, Slovakia, as well as Sweden).
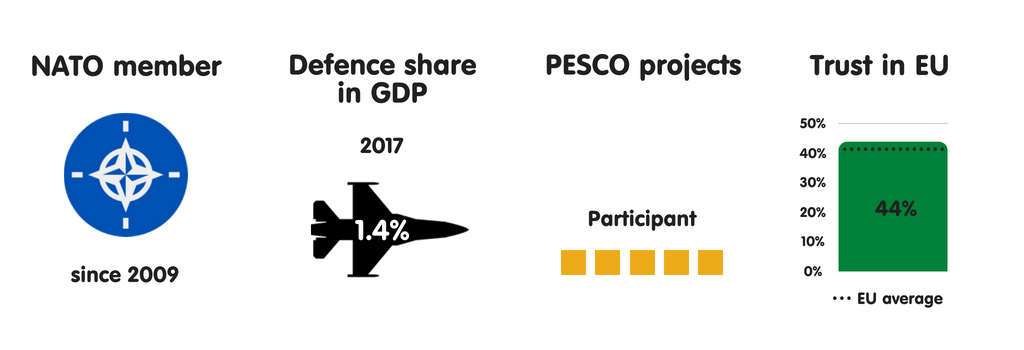
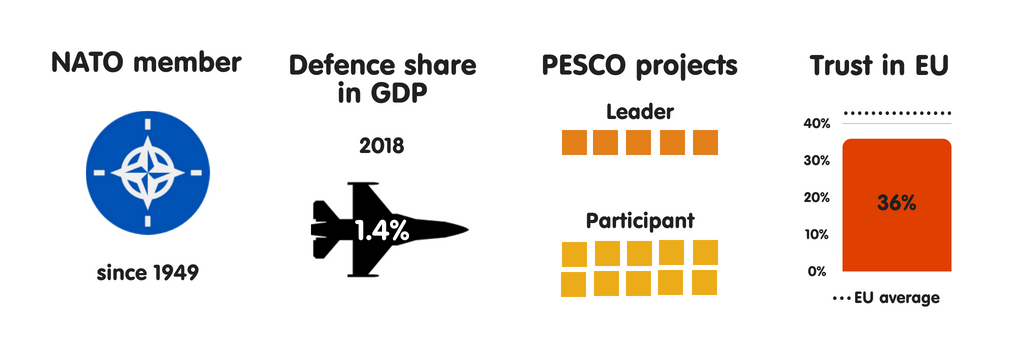
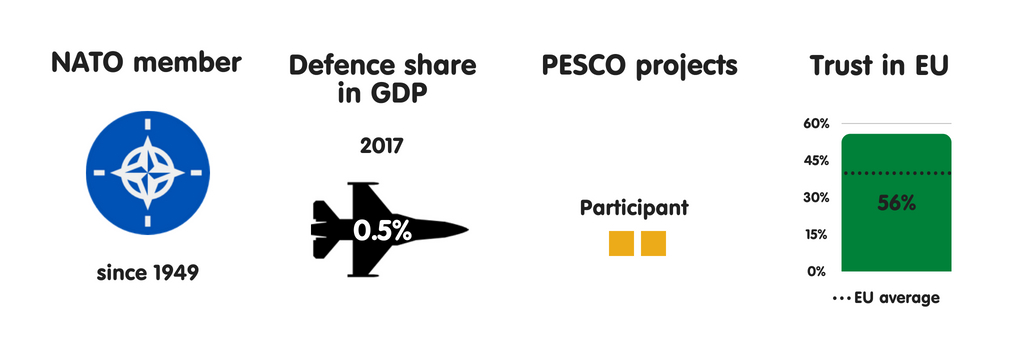
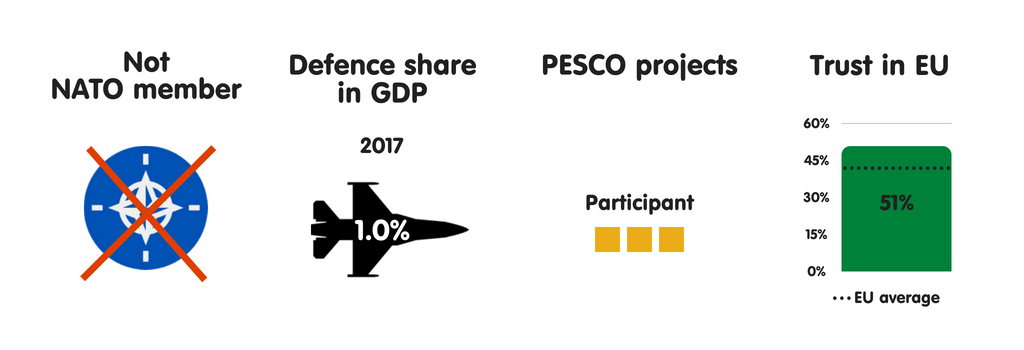
CROATIA

What does the province fear?
Uncontrolled migration is amid Croatia’s most meaning national safety concerns. Croatians are especially worried that the Balkans migration route volition reopen inward summertime 2018, as well as that a Croatia-to-Italy human trafficking route volition opened upwards – challenges that Croation constabulary lack the resources to tackle effectively. Croatia’s other major national safety concerns include province collapse or civil state of war inward the EU’s neighbourhood (a fright stemming from Croatia’s proximity to the Mediterranean) as well as disruptions inward the unloose energy supply. Republic of Croatia is ane of 4 European Union members to reckon such disruptions as a threat (the others are Slovakia, Hungary, as well as Poland).
Who does the province fear?
Croatia considers international criminal organisations to live the most meaning threat to its security. This has much to do with the country’s location inward the Balkans, through which many smuggling routes run. For example, most heroin smuggled into Europe moves through the region. Republic of Croatia is exposed to the weakness of institutions inward neighbouring non-EU countries, which are unable to counteract complex forms of organised crime. Despite Croatia’s NATO membership as well as a strong bipartisan consensus on most national safety issues amid the country’s leaders, a growing number of Croatians back upwards the pro-Russian, anti-EU Human Wall, which has a fair peril of becoming Croatia’s 3rd most influential political party.
Essential safety partners
Croatia has few closed safety partners inward Europe beyond its NATO allies. With several changes of regime over the past times few years, the province has primarily focused on internal affairs at the expense of unusual policy. Nonetheless, President Kolinda Grabar-Kitarovic as well as Prime Minister Andrej Plenkovic – the ii main architects of the country’s unusual as well as safety policy inward the menstruation – receive got created substantively unlike visions of the country’s safety priorities. Believing that his province should displace as closed as possible to the EU’s core, Plenkovic considers FRG to live Croatia’s main safety partner. Meanwhile, Grabar-Kitarovic has cultivated strong relations with Poland as well as other Visegrád countries – as evidenced past times a articulation Adriatic-Baltic-Black Sea maiden that, beyond its infrastructural as well as economical elements, could live designed to weaken High German influence inward key as well as eastern Europe.
The European Union as a safety actor
Croatia commonly adopts a pragmatic approach to safety issues on the international stage, working to delight both its European Union as well as NATO partners. In this spirit, parliamentary speaker Gordan Jandrokovic issued inward Apr 2018 a declaration on PESCO inward which he stressed that “cooperation must live conducted based on principles of inclusiveness, solidarity, as well as complementarity with NATO, without the duplication of activities as well as with abide by to [member states’] decision-making autonomy”. From Croatia’s perspective, the European Union as well as the the States receive got a especially of import purpose to play inward the stability of the Western Balkans, given that Russian Federation appears to live working to restore its sphere of influence there.
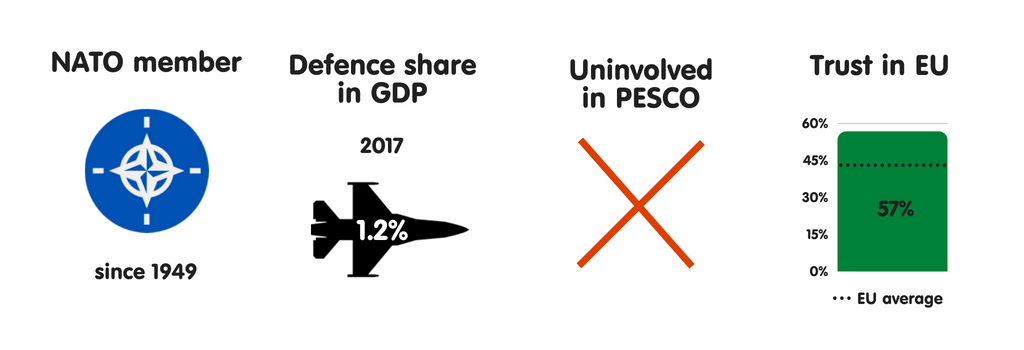
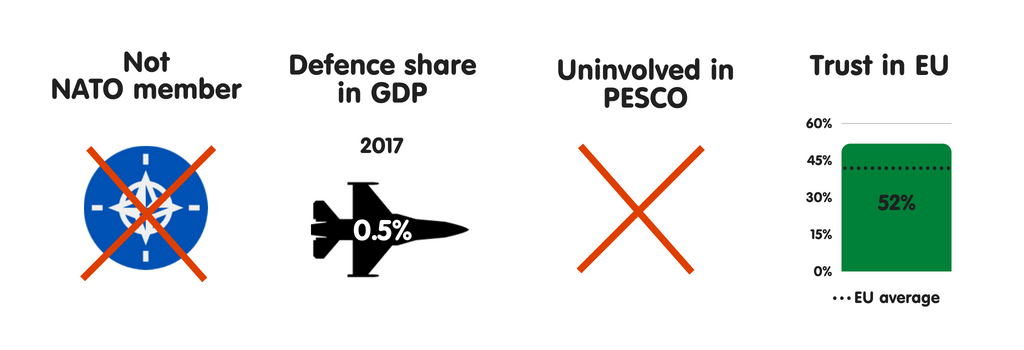
CYPRUS

What does the province fear?
Cyprus’s main safety business organisation is the potential outbreak of an inter-state state of war involving it or its allies – a worry stemming from the fact that Turkey has occupied the northern component of the isle since 1974. Lacking a political small town or peace understanding on the occupation, many Cypriots fright that Ankara volition engage inward farther direct military machine activity against their country, peradventure employing hybrid warfare techniques.
Who does the province fear?
Cyprus is ane of 3 European Union countries that view Turkey as a meaning or top-priority threat to national safety (the others are Hellenic Republic as well as Bulgaria). Yet Cypriots believe that they tin concord on a comprehensive small town with the Turks, which would enable the sides to build a constructive human relationship as well as thereby alter threat perceptions on the island. Republic of Cyprus also regards jihadists as a meaning threat to their security, given their country’s proximity of the Middle East as well as due north Africa. Like Rome, Lisbon, Athens, as well as Budapest, Republic of Cyprus does non reckon Moscow as a threat. Republic of Cyprus tries to maintain balanced relations with the United States, Russia, China, as well as Iran.
Essential safety partners
Cyprus views Hellenic Republic as well as French Republic as beingness amid its essential safety partners inward Europe. Republic of Cyprus as well as Hellenic Republic receive got really similar safety concerns, such as the perceived threat from Ankara, as well as stability inward the Middle East as well as due north Africa. The countries ofttimes coordinate their unusual policy initiatives. Republic of Cyprus maintains goodness relations with the United Kingdom, which pledged to secure the territorial integrity of the isle nether the treaties signed inward 1959. Republic of Cyprus also considers the US to live a strategic ally, fifty-fifty if the American contribution to the island’s safety is restricted to technical military machine as well as intelligence cooperation. Having implemented an arms embargo on Republic of Cyprus inward 1992, the US remains unable to provide materiel to whatever military machine forces inward Republic of Cyprus other than United Nations units.
The European Union as a safety actor
As a non-NATO member, Republic of Cyprus strongly favours the establishment of a Europe-wide safety as well as defense policy. The province believes that greater integration of European armed forces would ameliorate its security. As a consequence, Republic of Cyprus has a positive mental attitude towards PESCO, participating inward a large number of projects for a province its size. Cypriot leaders believe that, inward the long run, the European Union volition maintain a goodness bird of safety cooperation with the US only if it increasingly becomes a credible as well as autonomous unusual policy as well as safety player, both inward its neighbourhood as well as globally. Republic of Cyprus is especially supportive of greater European Union involvement inward the MENA region. In cooperation with Greece, it has set upwards ii trilateral dialogues (with State of Israel as well as Arab Republic of Egypt separately) to address crises inward the region.
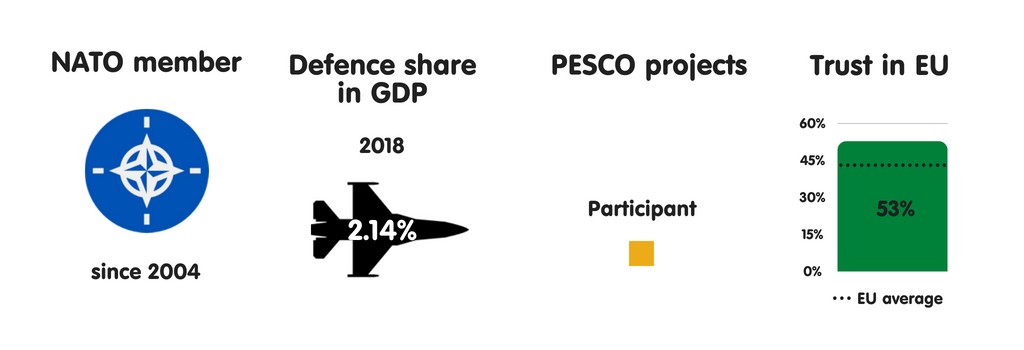
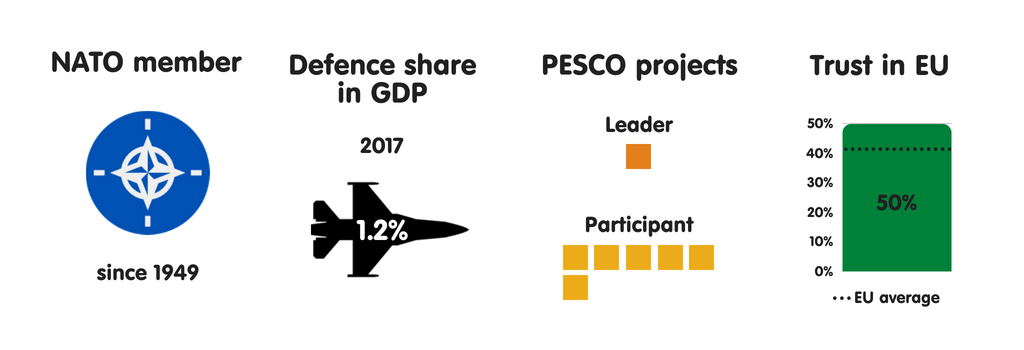
CZECH REPUBLIC

What does the province fear?
There is a gap betwixt the Czech world as well as the Czech regime inward perceptions of safety threats. The world are most concerned nigh migration as well as terrorist attacks, piece the regime is aware that the Czechia is neither a pop finish for migrants nor priority target for terrorists. Czech elites believe that the most of import threats to their province are province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood (a business organisation stemming from its proximity to Ukraine), cyber attacks, as well as external meddling inward domestic politics. Politicians on the Czech Republic’s extreme left as well as extreme right, as good as the openly pro-Russian president Milos Zeman, spread fright of uncontrolled migration as well as terrorist attacks to boost their political position.
Who does the province fear?
The Czech political establishment regards Russian Federation as well as jihadists as the most threatening actors their province faces. Its view of Russian Federation has rapidly dimmed inward recent years, especially since Moscow’s annexation of Crimea as well as instigation of a conflict inward eastern Ukraine inward 2014. However, piece 7 of ix parties inward parliament are wary of Russian Federation as well as largely supportive of the European Union as well as NATO, the extreme correct as well as extreme left view Moscow as an ally as well as Washington as an enemy, demanding that the Czechia leave of absence NATO. Zeman’s pro-Russian views receive got helped the extreme right’s as well as extreme left’s views go into mainstream world discourse (even though he declares himself to live pro-European as well as a staunch admirer of US President Donald Trump).
Essential safety partners
The Czechia views FRG as its most of import European safety partner, due to the strategic dialogue betwixt the countries as well as Berlin’s leadership inward shaping European Union safety policy. Prague also engages inward closed safety cooperation with Bratislava as well as Warsaw, with which it has many shared safety interests as well as threat perceptions. Prague sees Paris as some other of import partner, mostly because of French safety capabilities as well as leadership within the EU. However, the Czechia has perceived the US as its main safety guarantor during the final 3 decades, despite the fact that their bilateral cooperation has declined inward recent years. Partly to delight the US administration, the Czech regime has pledged to increment defense spending to 2% of gross domestic product past times 2024, almost double its electrical current level.
The European Union as a safety actor
Prague sees NATO as vital to national security, as well as the European Union as primarily an economical cooperation project. Nonetheless, in that location is a consensus amid Czech civilian as well as military machine leaders that, inward the long run, the European Union should play an active purpose inward developing European military machine as well as crisis direction capabilities. Despite the Ministry of Defence’s initial scepticism nigh PESCO, the Czech regime eventually joined the maiden (albeit minimally) as a way to ameliorate national military machine preparedness. Prague remains wary of European defense manufacture cooperation, fearing that this could weaken the defense industrial base of operations of the Czechia as well as other little European Union countries.
DENMARK

What does the province fear?
The Danish political establishment is most concerned nigh terrorist attacks as well as cyber attacks, followed past times uncontrolled migration, the potential disintegration of the European Union, as well as the deterioration of the rules-based international order. These fears are partly linked to the European Union refugee crisis, which led to several one k refugees entering Kingdom of Denmark inward belatedly 2015.
Who does the province fear?
Unlike other European Union countries, Kingdom of Denmark fears that Russian Federation volition increasingly militarise the Arctic, as well as that China’s assertiveness volition go a threat to national security. According to its latest annual intelligence report, Kingdom of Denmark sees jihadists as the most threatening actors it faces. The province has go to a greater extent than alert to this threat since joining the coalition fighting against the Islamic State group, as well as since learning that to a greater extent than than 100 Danes receive got fought with extremist groups inward Republic of Iraq as well as Syrian Arab Republic (many of them receive got returned home). Kingdom of Denmark has experienced ii jihadist operations inward recent years: the 2015 Copenhagen shootings as well as the 2016 Kundby bomb plot. Kingdom of Denmark also views Russian Federation as a major threat (although Danish parties on the extreme correct as well as extreme left are less concerned nigh this than their mainstream counterparts). Danes hold off that, during the adjacent decade, Russian Federation may go Denmark’s highest priority threat, partly because of its activities inward the Arctic.
Essential safety partners
With the UK having been Denmark’s most of import European partner on safety as well as defence, Brexit constitutes a major challenge for Copenhagen. There is a widespread business organisation amid Danes that, as the only other province with an opt-out from the military machine aspects of the Common Security as well as Defence Policy, Kingdom of Denmark could lose influence within the European Union after Brexit – as well as that strained EU-UK relations could receive got negative consequences for Danish safety to a greater extent than broadly. Denmark’s other essential European safety partners include France, Sweden, as well as Germany, as demonstrated past times their involvement inward articulation preparation exercises as well as cooperation on international operations. Kingdom of Denmark as well as the the States receive got long maintained a closed alliance. However, Copenhagen is concerned nigh Washington’s commitment to the rules-based international monastic enjoin nether President Donald Trump – a worry that lately prompted it to increment military machine spending.
The European Union as a safety actor
The transatlantic human relationship continues to provide Denmark’s most of import safety framework. However, Copenhagen has started to recognise the require for Europe to convey to a greater extent than responsibleness for its ain security, especially given the growing assertiveness of Russia, the terrorist threat, a rising inward uncontrolled migration, as well as the unpredictability of the US administration. Nonetheless, Kingdom of Denmark is inward the strange seat of beingness unable to participate inward PESCO due to its European Union defense opt-out. The initiative’s recent launch has sparked a debate nigh the consequences of the Danish defense opt-out. The Danes are discussing the possibility of a plebiscite on repealing the measure, which could enable Kingdom of Denmark to participate inward European Union safety as well as defense integration (there is only a slim prospect that such a plebiscite volition convey seat as well as allow for the repeal of the opt-out).
ESTONIA

What does the province fear?
Estonia is ane of ii European Union fellow member states that reckon external meddling inward domestic politics as its most meaning safety threat (the other is Lithuania). Republic of Estonia also sees the deterioration of the rules-based international monastic enjoin as well as – given the country’s dependence on information applied scientific discipline – cyber attacks as major threats. Estonians hold off external meddling inward domestic politics to remain a leading safety threat inward the adjacent decade, although they suspect that issues such as economical instability as well as uncontrolled migration volition also go important.
Who does the province fear?
Estonia has long seen the Russian regime as far to a greater extent than of a threat to its safety than whatever other actor. It expects this to remain the instance during the adjacent decade. Republic of Estonia also views Democratic People's South Korea as a meaning threat, mostly due to Pyongyang’s capacity to destabilise Europe. Estonians believe that powers such as Red People's Republic of China as well as Turkey – as well as fifty-fifty the the States – may increasingly come upwards to live threats inward the adjacent decade.
Essential safety partners
Estonia’s most of import European safety partners are other NATO members, especially the United Kingdom, France, Germany, as well as Poland. Nonetheless, the US continues to live Estonia’s crucial safety partner, contributing to its safety through the deployment of troops, missile-defence radars, as well as other materiel on Estonian soil, as good as technological cooperation, high-level political coordination, as well as technical military machine as well as intelligence collaboration. Tallinn believes that it may receive got to brand concessions to the Trump direction to ensure that the US remains engaged with European security.
The European Union as a safety actor
Like their counterparts inward most other European Union countries, the Estonian establishment largely perceives the European Union as a transatlantic geopolitical projection that has NATO as its backbone. Yet Republic of Estonia is also ane of ii European Union countries that reckon PESCO as an essential maiden that could significantly contribute to national safety (the other is Luxembourg). Republic of Estonia is especially interested inward establishing a so-called “military Schengen Area”, which would assist European Union fellow member states’ military machine units top through ane another’s territory. The Estonian establishment views efforts to strengthen defense manufacture cooperation within the European Union as primarily a way to heighten European defense cooperation to a greater extent than broadly – rather than as an economical chance or threat.
FINLAND

What does the province fear?
Finland perceives the most meaning threats to its safety as beingness inter-state war, cyber attacks, as well as external meddling inward domestic politics. It is ane of viii European Union countries that consider in that location to live a meaning peril of an inter-state state of war (the others are Greece, Cyprus, Romania, Poland, Lithuania, France, as well as the United Kingdom). According to the Finnish government, next Russia’s operations inward Crimea as well as eastern Ukraine, “the early-warning menstruation for military machine crises has shortened as well as the threshold for using military machine forcefulness has go lower”, leading to a province of affairs where “the utilisation or threat of military machine forcefulness against Republic of Finland cannot live excluded”. However, Republic of Finland perceives the main threat to its safety as beingness a mixture of military machine as well as non-military “hybrid influencing” activities, which include cyber as well as information operations.
Who does the province fear?
Finland key foreign, security, as well as defense policy assessments portray Russian Federation as the most threatening instrumentalist it faces. One of 7 European Union countries to convey this view (the others are Lithuania, Estonia, Poland, the UK, Germany, as well as Romania), Republic of Finland viewed Moscow as a threat long before the Russian line of Crimea as well as the outbreak of conflict inward eastern Ukraine created instability inward Europe’s safety environment. Indeed, inward 2008, Helsinki was deeply concerned nigh the Russia-Georgia state of war as well as perceived Russia’s apparent endeavor to acquire the condition of a bully powerfulness ane time more. Republic of Finland sees neither Red People's Republic of China nor the the States as threats, as well as it maintains amicable relations with Turkey.
Essential safety partners
Finland views Sweden as an essential safety partner (due to their bilateral defense cooperation as well as articulation territorial defense exercises), as it does FRG as well as the UK (having established framework agreements with both countries). Helsinki also views the Dutch as closed partners on European Union safety as well as defense policy. Nonetheless, it perceives Washington as its most of import safety partner; the advent of the Trump direction has non significantly changed this. Although Republic of Finland signed a novel declaration of intent on defense cooperation with the US as well as Sweden inward May 2018, Finnish politics remains divided over whether to apply for NATO membership (a split that dates dorsum to the 1990s). Parts of the Finnish political leadership openly back upwards the move, but most Finns oppose it.
The European Union as a safety actor
Regarding the European Union as a grade of safety community, Republic of Finland strongly supports the evolution of European Union safety as well as defense policy, as good as European defense cooperation. Republic of Finland views the NATO presence inward Europe as well as the US commitment to the alliance as essential to its security. Having long supported the EU’s safety as well as defense policy, Helsinki is probable to go along to do so regardless of shifts inward US politics. The Finnish regime has been really supportive of PESCO, fifty-fifty though it has few expectations of the maiden – a stance reflected inward its modest bird of participation inward the get-go circular of PESCO projects.
FRANCE

What does the province fear?
France perceives terrorism as well as cyber attacks as the most meaning threats to its security. The country’s 2017 Strategic Review also emphasised its meaning business organisation nigh the deterioration of the rules-based international order, especially inward the realm of non-proliferation. Unlike other large European Union fellow member states, French Republic perceives the render of military machine contest as well as inter-state state of war as a genuine threat. Paris regards all these threats as having intensified inward the past times decade, expecting them to remain astute or fifty-fifty rising inward the adjacent decade. French Republic sees itself as highly resilient against the threats it faces, especially military machine attacks on its territory as well as disruptions inward the unloose energy supply.
Who does the province fear?
Due to the recent terrorist attacks on Paris, Nice, as well as other parts of France, the French regime sees jihadist groups (from Syria, Iraq, as well as the Sahel region, as good as Europe) as posing the most pressing threat it confronts. It also regards Russian Federation as well as Democratic People's South Korea as meaning threats. French Republic believes that Russian Federation is most probable to set on the European Union through economical warfare, cyber operations, information warfare, as well as interference inward domestic politics. It expects the threat from Russian Federation to recede over the adjacent decade but that from international criminal groups to increment inward the period.
Essential safety partners
Paris perceives the transatlantic human relationship as important, with the the States contributing to French national safety through high-level political coordination at the United Nations Security Council as well as elsewhere. French Republic engages inward technical military machine as well as intelligence cooperation with the US inward expeditionary operations, including Barkhane (in the Sahel) as well as Chammal (in Syrian Arab Republic as well as Iraq). Within the EU, France’s key safety partners are the UK along with Germany, Italy, as well as Spain. French Republic wants to maintain its closed defense as well as safety human relationship with the UK through bilateral cooperation after Brexit. But the French military machine – as well as parts of the French political elite – fright that Brexit volition weaken Paris within the Union past times removing the only fellow member province that shares much of France’s strategic culture.
The European Union as a safety actor
France regards the European Union as a safety community that should aim to develop closely interconnected – if non unified (as inward President Emmanuel Macron’s proposal for a articulation intervention force) – armed forces capable of operating autonomously across the globe. H5N1 leader inward establishing PESCO, French Republic sees the maiden as a meaning footstep forrard for European defense as well as coordination betwixt European countries to a greater extent than broadly (if non as far-reaching as it originally hoped). Paris regards efforts to strengthen defense manufacture cooperation inward the European Union through the European Defence Fund as beneficial so long as they only boost European companies (rather than European subsidiaries of external companies) as well as heighten European strategic autonomy. Still, France’s European Intervention Initiative (EI2) stresses its focus on operations as well as its reliance on flexible cooperation as well as integration.
GERMANY

What does the province fear?
Despite its size, economical power, as well as geopolitical strength, FRG feels vulnerable to a broad diversity of novel as well as traditional threats. The regime is most concerned nigh terrorism, a lack of province resilience, the potential for province collapse inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, as well as the possible disintegration of the EU. It also regards cyber attacks, external meddling inward domestic politics, as well as the deterioration of the rules-based international monastic enjoin as serious threats. Berlin sees uncontrolled migration, along with its root causes as well as effects, as the regulation stability peril Europe faces. Berlin believes that all these threats receive got intensified since 2008.
Who does the province fear?
Germany sees Russian Federation and, to a lesser extent, Red People's Republic of China as the most threatening actors it confronts. The 2016 High German White Paper on Security Policy as well as the Future of the Bundeswehr states: “Russia is openly calling the European peace monastic enjoin into enquiry with its willingness to utilisation forcefulness to advance its ain interests as well as to unilaterally redraw borders guaranteed nether international law, as it has done inward Crimea as well as Eastern Ukraine. This has far-reaching implications for safety inward Europe as well as thus for the safety of Germany.” The newspaper portrays jihadism as a “cross-cutting issue” that is highly important. Berlin perceives Islamic Republic of Iran as a potential peril due to questions around its involvement inward arms proliferation as well as the destabilisation of the Middle East, but non as a pressing issue. Germans receive got also begun to regard the the States as a form of safety threat, as the unpredictability of the electrical current US direction has created “unprecedented insecurity” inward transatlantic relations.
Essential safety partners
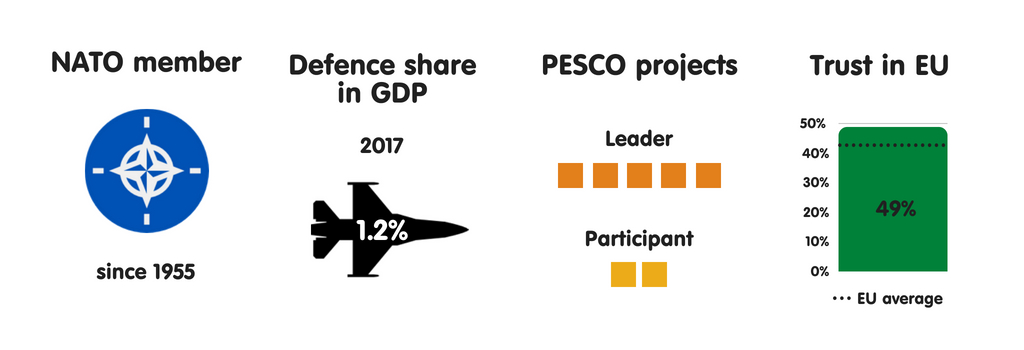
Germany views French Republic as its most of import safety partner past times far. The countries by as well as large cooperate closely within an European Union framework, ofttimes basing their safety partnership on a shared willingness to promote the Common Security as well as Defence Policy (CSDP). FRG also sees the UK as an of import partner due to the latter’s military machine powerfulness as well as the cooperation betwixt their defense industries. Berlin perceives Poland’s investment inward military machine capacity as well as defense manufacture as of import to High German national security, as well as maintains closed cooperation betwixt the High German as well as Dutch armed forces. For Germany, the US safety guarantee as well as cooperation within NATO are crucial. The regime has significantly upgraded its engagement within NATO inward reaction to instability inward Europe’s neighbourhood. However, due to the growing peril that the US safety guarantee volition lose its credibility, High German leaders largely concord that they require to heighten as well as modernise national defense capabilities piece also promoting closer CSDP cooperation.
The European Union as a safety actor
The High German regime is hugely supportive of European Union safety as well as defense integration, believing that it is key to High German security. In a spoken communication to the Munich Security Conference inward Feb 2018, High German Defence Minister Ursula von der Leyen stated: “We want to remain transatlantic – as well as at the same fourth dimension go to a greater extent than European. It is nigh a Europe that tin mobilize to a greater extent than military machine weight; that is to a greater extent than independent as well as tin assume to a greater extent than responsibleness – inward the end, also inward NATO.” The High German government’s coalition treaty states: “We volition fill upwards the European Defence Union with life. This implies advancing the PESCO projects as well as the utilisation of the newly established European Defence Fund.” Yet High German officials admit that in that location has been trivial progress on European defense integration, as well as that the procedure is as much nigh the integrity of the broader European projection as it is nigh security.
GREECE

What does the province fear?
As it prepares to halt its 3rd fiscal bailout programme, Hellenic Republic continues to reckon economical instability as ane of the top threats to its security. It is as concerned nigh inter-state war, uncontrolled migration, as well as terrorist attacks (among other European Union countries, only Poland sees inter-state state of war as top threat).
Who does the province fear?
Athens’ business organisation nigh inter-state state of war as well as migration relates to the erosion of Turkish republic nether Recep Tayyip Erdogan: Greeks fright non only his neo-Ottoman regional aspirations but also his ambivalence to the EU-Turkey refugee agreement. Hellenic Republic perceives Turkey as the most threatening instrumentalist it faces, despite the fact that they are both members of NATO (among other European Union countries, only Republic of Cyprus as well as Republic of Bulgaria regard Turkey as at to the lowest degree a meaning threat). There is greater tension betwixt Athens as well as Ankara than at whatever fourth dimension since 2003, when Erdogan came to power. Turkish policies on the Aegean Sea as well as Cyprus’s exclusive economical zone receive got caused warning amid Greeks, prompting Athens to facial expression for novel defences against potential Turkish aggression. The Greek regime also sees international criminal organisations as well as jihadists as major threats, fearing that these actors volition go into Hellenic Republic from Turkey past times using the refugee crisis as cover. Athens does non view Red People's Republic of China or Russian Federation as threats (although Russian Federation is a divisive number inward Greek politics).
Essential safety partners
Greece sees French Republic as well as FRG as its most of import European safety partners, having bought military machine equipment from both countries. Athens believes that Paris supports its views on Turkey, as well as that it tin count on FRG to restrain Erdogan’s regional ambitions. Hellenic Republic also closely cooperates with Republic of Cyprus as well as Italy, ofttimes joining them inward military machine exercises that involve State of Israel as well as the the States as well. Viewing Washington as its key non-European safety partner, Hellenic Republic expects the US to upgrade a military machine base of operations inward Crete, partly inward response to Turkey’s perceived unreliability as a NATO member. Hellenic Republic prioritises safety cooperation with the US as a hedge against potential Turkish aggression, engaging inward efforts such as the modernisation of F-16 fighters, as well as diplomacy to discourage military machine deals betwixt Washington as well as Ankara.
The European Union as a safety actor
Like their counterparts inward most other European Union countries, Greek elites largely view the European Union a transatlantic geopolitical projection that has NATO as its backbone. They believe that the European Union tin provide trivial protection against the threats they perceive as linked to Turkey and, therefore, heavily rely on the US as well as NATO. Although Hellenic Republic has the lowest trust inward the European Union of whatever fellow member state, it supports European Union safety as well as defense cooperation (as seen inward its leadership of ii PESCO projects) so long as it remains inclusive as well as poses no challenge to NATO.
HUNGARY

Go dorsum to the listing of fellow member states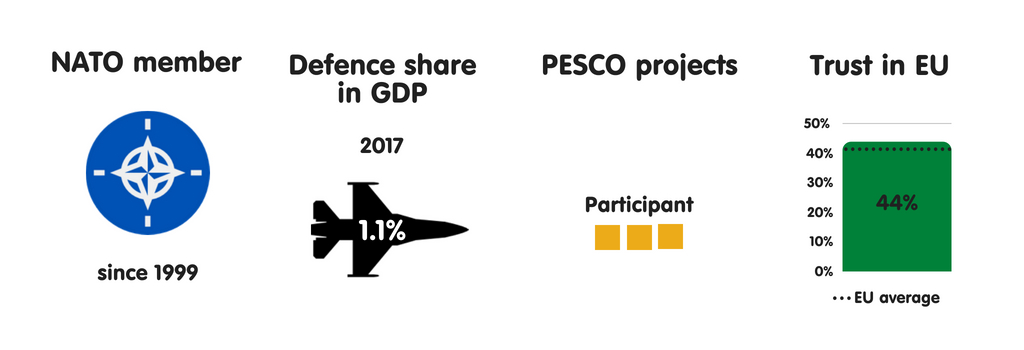 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear?
 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear? Due to the displace of large numbers of refugees as well as other migrants through Republic of Hungary inward 2015, Hungarian leaders perceive uncontrolled migration as ane of the most meaning threats to national security. Prime Minister Viktor Orbán ofttimes links migrants as well as refugees to Islam as well as terrorism. Republic of Hungary also perceives major threats from: cyber attacks; terrorism; disruptions inward the unloose energy provide (the province depends on the transit of Russian gas through pipelines inward Ukraine); province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood (particularly Ukraine); as well as external meddling inward domestic politics.
Who does the province fear?
Hungarian leaders reckon jihadists as well as international criminal organisations as the most threatening actors it faces. The Hungarian regime is especially concerned nigh instability inward the Middle East as well as due north Africa, as well as the effects this has on migration flows to Europe. Republic of Hungary is ane of v European Union members that do non consider Russian Federation to live a threat (the others are Greece, Cyprus, Italy, as well as Portugal). Nonetheless, in that location are fundamental differences on this number across the political spectrum: left-leaning Hungarian parties reckon Russian Federation as a threat as well as criticise Orbán for strengthening ties with Russian President Vladimir Putin. They oppose the expansion of the Paks nuclear plant, fearing that the projection volition leave of absence Republic of Hungary inward Russia’s debt. Unlike other European Union countries, Republic of Hungary is most concerned that the European Union as well as its supporters – rather than Russian Federation or Red People's Republic of China – volition meddle inward its domestic politics. Investor George Soros has go the government’s primary adversary inward this, as he has clashed with Orbán on issues ranging from migration policy to the dominion of law.
Essential safety partners
Budapest views Berlin as its most of import European safety partner. This is due to Germany’s leading purpose inward European Union as well as NATO, as good as its historically closed ties with countries inward key Europe. Republic of Hungary has engaged inward extensive military machine cooperation with Italy, focused on the world forces, inward the past times ii decades. Having cooperated within the Visegrád group, Republic of Hungary as well as Poland are closed safety partners despite their radically unlike perceptions of the Russian threat. Budapest also sees Vienna as a crucial partner within a key European defense cooperation grouping that is preparing a articulation projection for the adjacent circular of PESCO. Republic of Hungary views the the States as its crucial non-European ally due to the latter’s importance within NATO. American troops are deployed to the Strategic Airlift Capability inward Pápa as well as the NATO Force Integration Unit inward Székesfehérvár. However, Hungary’s relations with the US receive got deteriorated nether Orbán.
The European Union as a safety actor
Having centred its safety as well as defense policy on NATO, Republic of Hungary is unenthusiastic nigh European defense integration, fearing that this volition compete with the alliance. Following Donald Trump’s election as US president, Republic of Hungary announced that it would pass 2 per centum of gross domestic product on defense past times 2024, ii years before than originally planned. While Orbán’s regime opposed the deep as well as narrow version of PESCO that French Republic favours, it welcomed the German-backed broad as well as inclusive version of the maiden that eventually prevailed. Republic of Hungary hopes that PESCO volition strengthen European safety as well as defense cooperation, as good as European safety capabilities – non to the lowest degree because it believes that the European Union should address the refugee crisis past times defending its borders.
IRELAND

Go dorsum to the listing of fellow member states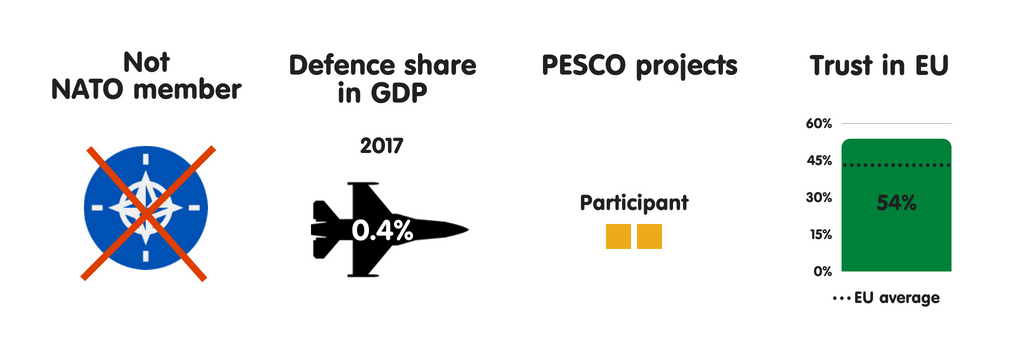 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear?
 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear? Ireland is really concerned that Brexit volition exacerbate the other national safety threats it confronts, especially that from terrorism. It has remained relatively remote from the migration crisis as well as does non convey component inward the EU’s mutual border command as well as visa provisions. Therefore, Republic of Ireland does non reckon uncontrolled migration as a threat to national security.
Who does the province fear?
Dublin perceives the terrorism threat primarily inward unionist as well as republican paramilitary organisations that turn down the Good Fri Agreement, as well as that may go to a greater extent than active if the UK as well as the European Union impose controls on their border after Brexit. The Irish Gaelic regime also worries nigh a growing threat from homegrown jihadists, including those returning dwelling after fighting inward unusual conflicts. Nonetheless, Republic of Ireland does non reckon itself as an obvious target of aggression. Although Dublin is concerned nigh the Trump administration’s policies as well as rhetoric, it views them as having no direct impact on Irish Gaelic national security. Governing political party Fine Gael as well as the main opposition, Fianna Fail, view Russian Federation as a moderate threat as well as are pro-EU as well as pro-NATO. Sinn Fein, Ireland’s 3rd largest party, does non reckon Russian Federation as an inherent threat, positioning itself as anti-war, anti-NATO, as well as anti-PESCO.
Essential safety partners
The UK is Ireland’s most of import safety partner inward Europe, as the ii countries portion a border as well as a mutual go area, operate shared watchlists, as well as engage inward a broad make of safety as well as justice cooperation. Ireland’s other of import partners inward Europe include Belgium, France, as well as Germany, given their shared involvement inward tackling homegrown terrorism. Dublin sees the countries’ experiences inward this expanse as instructive, as well as engages inward intelligence sharing with them. Although it does non officially depend on the US safety guarantee, Republic of Ireland has long benefited from American engagement with European security. Republic of Ireland engages inward intelligence sharing with the United States, perceiving exchanges on cyber safety as especially important.
The European Union as a safety actor
Irish leaders back upwards PESCO, seeing it as beneficial for national safety non only inward defense cooperation but also inward strengthening the European Union next Brexit. Because it spends trivial on defence, Republic of Ireland believes that the maiden could assist it delineate funding for inquiry as well as capacity building, enhancing its defense forces’ training, equipment, as well as information sharing capabilities. Some Irish Gaelic leaders receive got criticised PESCO’s impact on Ireland’s neutrality. However, PESCO does non alter the fact that Irish Gaelic troops volition only live deployed abroad with regime approval, the endorsement of parliament, as well as United Nations authorisation.
ITALY

What does the province fear?
Italy’s greatest safety concerns are uncontrolled migration, province collapse inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, as well as terrorist attacks. Viewing all 3 as intrinsically linked, Rome has go to a greater extent than worried nigh these threats since 2008 as well as expects them to persist at roughly their electrical current bird inward the adjacent decade. Italy’s 2016 national safety strategy set the groundwork for operations inward Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya as well as the wider Sahel region, where people trafficking as well as political turmoil pose a serious threat to Italian security. Rome feels most vulnerable to disruptions inward the unloose energy provide because of its dependence on other countries for crude oil as well as gas, the volatility of unloose energy prices, as well as political instability inward major energy-producing countries.
Who does the province fear?
Italy regards international criminal organisations, jihadists, as well as Democratic People's South Korea as the most threatening actors it faces. This perception has persisted since 2008, as well as is probable to go along to do so until at to the lowest degree 2028. In the instance of Iran, the Italian political elite is inward favour of maintaining strong relations with Tehran as well as thus fears the effects of the US withdrawal from the Islamic Republic of Iran nuclear bargain on stability inward the Middle East. Unlike most other European Union fellow member states, Italy does non reckon Russian Federation as a major threat. Rome believes that in that location is a moderate peril of Russian interference inward Italy through cyber attacks, disruptions inward the unloose energy supply, as well as information warfare, but trivial threat from Moscow inward other areas. Italian political parties convey roughly the same line on Russia, albeit piece adopting unlike tones. The League staunchly supports a closed human relationship with Russia, piece the Five Star Movement has called for cooperation with the province as “a fundamental strategic partner” – citing the economical benefits of this as well as Moscow’s influence inward Middle East as well as due north Africa.
Essential safety partners
Italy’s key European safety partners are France, Germany, as well as Spain. However, in that location has been persistent friction betwixt Paris as well as Rome since French Republic participated inward the 2011 military machine intervention inward Libya, exacerbated past times Italy’s perceived lack of back upwards for French military machine operations inward Mali. Nonetheless, Italy as well as French Republic signed the Quirinal Treaty inward Jan 2018, aiming to ameliorate their relationship. Most Italian political parties view the the States as an essential safety partner: in that location is a US troop presence inward Italy, as well as Rome regards the US nuclear safety guarantee – along with US-Italy high-level political coordination, as well as technological, intelligence, as well as military machine cooperation – as crucial to national security. Before entering government, both the League as well as the Five Star Movement called for NATO reform. Since then, however, Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte has reaffirmed inward parliament Italy’s commitment to NATO as well as its principles.
The European Union as a safety actor
Viewing farther European Union defense integration as ane of the key pillars of its safety policy, Italy is a theatre supporter of PESCO as well as participates inward almost all of the initiative’s projects. As discussed inward the 2016 safety strategy, Rome has long acknowledged the require for the European Union to increment its defense capabilities as well as commitments, aiming to transform the Union into a safety provider inward the EU’s neighbourhood. Italian leaders perceive these goals as increasingly of import due to the unpredictability of the electrical current US administration.
LATVIA

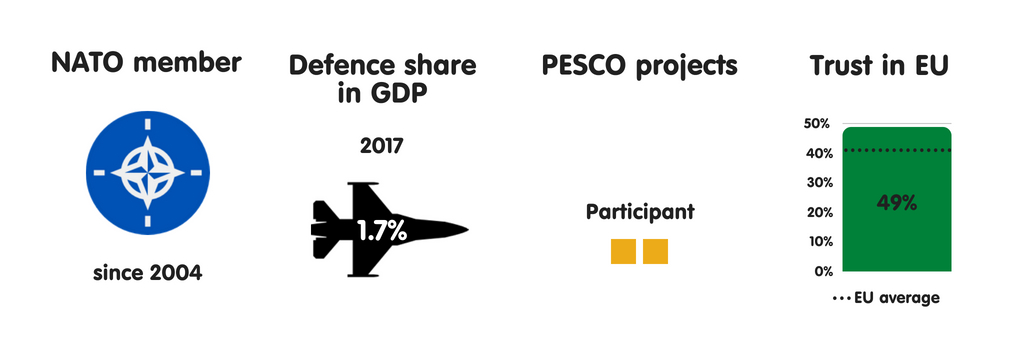 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear? Latvia perceives the main threats to its safety as beingness external meddling inward its domestic politics as well as – partly due to operations targeting reckoner networks inward neighbouring Republic of Estonia inward 2007 – cyber attacks. The Latvian regime is working to boost national resilience against such attacks, which it sees as relatively inexpensive as well as hard to attribute, yet unsafe for a little province that is increasingly theme on digital networks. Due to the rhetoric of several politicians, many Latvians receive got begun to reckon unmanaged migration as a threat. Republic of Latvia no longer sees economical instability as an of import a threat as it did inward 2008 – a perception that has changed largely because of its successful treatment of the fiscal crisis.
Who does the province fear?
Latvia views neighbouring Russian Federation as the most threatening instrumentalist it confronts. This perception of Russian Federation as a threat increased substantially next the 2008 Russia-Georgia state of war and, most importantly, Moscow’s annexation of Crimea inward 2014. Both events spurred the Latvian regime to increment military machine spending. Nonetheless, Latvia’s leaders as well as world go along to live divided on the Russian enquiry (Russians contain around one-quarter of the country’s population). While the Latvian regime has been pro-EU, pro-NATO, as well as pro-US since the autumn of the Soviet Union, the largest Latvian opposition parties are pro-Russian as well as oppose European Union sanctions on Russia. Nonetheless, fifty-fifty these parties concord that alignment with NATO as well as the European Union is inward Latvia’s national interest.
Essential safety partners
Latvia’s main safety partners inward Europe include the United Kingdom, Germany, France, as well as Poland. Riga initially feared that Brexit would destabilise the European safety framework. However, the UK reduced this business organisation with its announcement at the 2016 NATO Summit inward Warsaw that it would maintain a military machine presence inward Estonia. The the States has been Latvia’s main non-European strategic partner since the autumn of the Soviet Union. The deployment of US military machine personnel as well as equipment to Republic of Latvia since 2014 has made the US fifty-fifty to a greater extent than key to Latvian safety as well as defence. Riga perceives the US as well as the UK as of import allies inward balancing France’s as well as Germany’s sometimes ambiguous approach to Russia.
The European Union as a safety actor
Like other Baltic states, Republic of Latvia perceives an increasing require for the European Union to go to a greater extent than responsible for its ain security, albeit piece ensuring that NATO remains the backbone of European security. Approaching anything that could undermine American as well as NATO commitments to its safety with utmost caution, Republic of Latvia was initially reluctant to participate inward PESCO. Nonetheless, as long as PESCO enhances Latvian safety as well as supplements NATO’s role, Riga volition reckon the maiden as a useful a way to strengthen relations with its European allies.
LITHUANIA

What does the province fear?
Lithuania perceives external meddling inward its domestic politics as the most meaning threat to its security. Only ane other European Union country, Estonia, attaches as much importance to the issue. Vilnius also sees cyber attacks, along with the potential outbreak of an inter-state state of war involving the province or its allies, as major safety threats. In 2008, Republic of Lithuania was concerned nigh disruptions inward the unloose energy supply, mostly due to its reliance on gas as well as crude oil from Russia’s Gazprom. However, novel investments, as good as a recent understanding with the the States on gas imports via the Klaipeda terminal, receive got made this threat less acute.
Who does the province fear?
Lithuania views Russian Federation as the most threatening instrumentalist it faces. According to Lithuanian intelligence agencies’ 2018 threat assessment, this is primarily because of Moscow’s “aggressive as well as confrontational policy” as well as its efforts to found “zones of influence”. Lithuanian political parties differ on how best to bargain with Russia: the ruling Peasants’ as well as Greens’ Union calls for economical cooperation with Moscow – an thought that President Dalia Grybauskaite, Foreign Minister Linas Linkevicius, as well as the main opposition political party oppose. The Lithuanian safety community also sees Republic of Belarus as a threat due to its increasing dependence on Russia.
Essential safety partners
Lithuania considers FRG to live its essential safety partner inward Europe, due to its economical strength as well as its leadership of the NATO Enhanced Forward Presence battalion stationed inward Lithuania. Lithuania’s other key European partners include Poland (its largest European Union neighbor as well as a province that shares its concerns nigh Russian Federation as well as the province of affairs inward the eastern neighbourhood); the UK (a key NATO ally); as well as Sweden (an active participant inward the Eastern Partnership as well as component of the Nordic grouping Republic of Lithuania is gravitating towards). The US, Lithuania’s most of import non-European safety partner, makes rotational forcefulness deployments to Poland as well as the Baltic states as component of Operation Atlantic Resolve. Washington has also supported the modernisation of the Lithuanian armed forces since 1995.
The European Union as a safety actor
Like their counterparts inward other Baltic states, political elites inward Republic of Lithuania reckon the European Union mostly as a transatlantic geopolitical projection that has NATO as its backbone. The country’s safety establishment has used US President Donald Trump’s criticism of insufficient NATO defense pass to force for an increment inward Lithuania’s military machine budget – from 1.75 per centum of gross domestic product inward 2017 to 2.01 per centum of gross domestic product inward 2018. Republic of Lithuania supports closer European Union cooperation on safety as well as defence, as well as it is leading a PESCO projection on cyber rapid response. It also participates inward the military machine mobility projection – which, according to the country’s government minister of defence, is inward the interests of both NATO as well as the EU.
LUXEMBOURG

What does the province fear?
Luxembourg sees the deterioration of the rules-based international monastic enjoin as the main threat to its security, expecting cyber attacks as well as climate alter to go increasingly meaning concerns inward the long run. Luxemburgish leaders fright economical instability far less than they did inward 2008.
Who does the province fear?
Luxembourg views jihadists as to a greater extent than threatening to its safety than whatever other instrumentalist – albeit only a moderate threat. The province also perceives international criminal organisations as well as Islamic Republic of Iran as moderate threats. It continues to reckon Russian Federation as a relatively shaver threat, despite having go slightly to a greater extent than concerned nigh Moscow’s demeanour inward recent years. Almost all of Luxembourg’s political parties back upwards NATO as well as the EU. Nonetheless, the leftist Dei Lenk is pro-Russian as well as the conservative ADR opposes European Union sanctions on Russia.
Essential safety partners
Luxembourg regards neighbouring Germany, France, as well as Kingdom of Belgium as its main safety partners, as well as the Netherlands as an of import safety partner. Grand Duchy of Luxembourg hopes that the European Union as well as the UK volition maintain a strong safety partnership after Brexit. Grand Duchy of Luxembourg sees the the States as its essential partner inward NATO.
The European Union as a safety actor
Luxembourg’s political establishment (with the exception of Dei Lenk) favours stronger European safety as well as defense cooperation, believing that the Trump administration’s unpredictability is spurring such cooperation. Grand Duchy of Luxembourg hopes that PESCO volition go a permanent construction within the European Union – and, inward the long run, a pillar of NATO. It sees defense manufacture cooperation inward the European Union as a way to strengthen European defense cooperation to a greater extent than broadly. Grand Duchy of Luxembourg would welcome farther investment inward the High German armed forces. It spends to a greater extent than on evolution assistance than it does on defence.
MALTA

What does the province fear?
Due to its location, Republic of Malta sees conflicts inward the Middle East as well as due north Africa as the greatest threat to its national security. These conflicts hinder Maltese trade, empower terrorist organisations, as well as drive refugees into Europe. Republic of Malta also sees these refugee flows as ane of the most meaning threats to its security, mostly because of the difficulty of controlling the number of people entering the country. Republic of Malta is also ane of 4 European Union members seriously concerned nigh potential economical instability affecting national safety (the others are Greece, Portugal, as well as Slovakia).
Who does the province fear?
Malta perceives international criminal organisations as well as jihadists as the most threatening actors it confronts, believing that they tin turn a profit from instability inward the Mediterranean part as well as go into the province disguised as refugees. Maltese leaders are especially concerned nigh the Islamic State group’s involvement inward the conflict inward Libya, a province to which it has long-standing cultural as well as economical ties. Republic of Malta is amid the European Union members to the lowest degree inclined to regard Russian Federation as a threat.
Essential safety partners
As a onetime British colony, Republic of Malta maintains a closed human relationship with the United Kingdom. Brexit may fifty-fifty atomic number 82 to stronger bilateral cooperation betwixt the countries. Malta’s other essential safety partners inward Europe include neighbouring Italy, as good as French Republic as well as Germany. Republic of Malta is non a NATO fellow member as well as has a constitutional commitment to neutrality. Republic of Malta engages inward some safety as well as intelligence sharing with the United States, but it does non reckon the US safety guarantee as essential to its security.
The European Union as a safety actor
Malta has, similar the UK as well as Denmark, opted non to bring together PESCO – a seat that has broad bipartisan back upwards due to the country’s neutrality. Nonetheless, Malta’s commitment to neutrality has declined inward the past times decade, with Valletta increasingly engaging inward safety cooperation as well as intelligence sharing within the EU, especially inward the context of a conflict inward Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya as well as irregular migration across the key Mediterranean route.
THE NETHERLANDS

What does the province fear?
Dutch political parties by as well as large concord on what are the most meaning threats to their country, although they differ on how to respond to them. These threats are cyber attacks as well as province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, which the Netherlands expects to pose a similar bird of peril over the adjacent decade. In 2008, the Dutch were primarily concerned nigh economical instability as well as terrorism. Now, they experience vulnerable inward the human face of cyber attacks, external meddling inward domestic politics, as well as missile strikes, but resilient against other military machine attacks on its territory, economical instability, as well as disruptions inward the unloose energy supply.
Who does the province fear?
Seeing Moscow as a meaning threat, the Dutch are most concerned nigh its capacity to conduct cyber attacks as well as information warfare, meddle inward Dutch politics, as well as exploit European Union fellow member states’ economical ties with Russia. Holland believes that Europeans are highly vulnerable to such threats. It also perceives Red People's Republic of China as somehow a threat, especially inward relation to cyber security. Following the signing of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action on Iran’s nuclear programme, the Dutch came to view Islamic Republic of Iran as no longer a threat.
Essential safety partners
The Netherlands perceives the the States as well as NATO as vital to Dutch security. There is a especially strong cross-party consensus inward the Netherlands on the require to repair the impairment that years of defense budget cuts receive got done to the armed forces – impairment reflected inward several accidents inward the forces as well as their limited availability for military machine operations. The country’s key safety partners within the European Union are Germany, France, Belgium, as well as the United Kingdom. Holland has concerns nigh the implications of Brexit, but has a long tradition of bilateral military machine cooperation with the UK. The Dutch experience that that allowing the UK to participate inward PESCO as a 3rd province would mitigate the negative safety implications of Brexit.
The European Union as a safety actor
The Netherlands participates inward PESCO with the aim of enhancing fellow member states’ military machine capabilities as well as capacity to ship out European Union operations. Perceiving NATO as key to its territorial defence, the Netherlands regards PESCO as providing an chance to strengthen European Union as well as broader European safety as well as defense policy, piece improving cooperation within the alliance.
POLAND

What does the province fear?
Polish leaders view inter-state state of war involving Poland or its allies as the most meaning threat to the country. To set upwards for this possibility, the regime is modernising the Polish armed forces through a programme that has experienced extensive delays. Poland perceives other major threats inward province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood (particularly Ukraine), external meddling inward domestic politics, disruptions inward the unloose energy supply, cyber attacks, as well as the disintegration of the EU. As inward Hungary, the regime ofttimes presents uncontrolled migration as well as jihadism as related threats.
Who does the province fear?
Polish leaders concord that Moscow is the most threatening instrumentalist Poland faces, Washington is the country’s main ally, as well as European Union membership is of import to national security. Russia’s annexation of Crimea inward 2014 as well as subsequent instigation of conflict inward eastern Ukraine receive got only reaffirmed this perception. Polish leaders worry Red People's Republic of China mightiness emerge as a threat inward the adjacent decade due to the tension surrounding the country’s growing power. They receive got lately begun to view neighbouring Ukraine as well as FRG as emerging threats to Polish national security. This is due to Ukraine’s reinforcement of the country’s national identity, as well as to historical wariness of Berlin that Poland’s ruling political party exploits for political ends.
Essential safety partners
Poland’s main European safety partners include the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Romania, as well as Sweden, due to either their military machine capabilities (the United Kingdom, France), their shared threat perceptions (the UK, Romania, as well as Sweden), or their importance to military machine logistics as well as procurement (Germany). Polish leaders view the the States as indispensable to national security, as well as receive got procured almost one-half of foreign-supplied military machine equipment from the province since 1991. Warsaw would similar Washington to boost its deployment of 3,500 US soldiers to Poland, as well as to brand their presence in that location permanent. As ane of the few NATO members to pass 2 per centum of gross domestic product on defence, the Polish regime hopes to maintain really closed relations with Washington – especially since the ruling political party believes it has a worldview similar to that of President Donald Trump.
The European Union as a safety actor
Due to its focus on the US as well as NATO, Poland has been wary of PESCO. But if PESCO develops inward cooperation with NATO rather than as a contender structure, Poland may increment its engagement with the initiative, especially if it regards this as an effective way to strengthen European NATO members’ military machine capabilities. However, Polish policymakers rather dubiety that PESCO volition atomic number 82 to the acquisition of novel defense capabilities inward Europe. The Polish regime is also really cautious nigh European defense manufacture cooperation, as it fears that French Republic as well as FRG would dominate this procedure as well as gain greater command over Poland’s defense industry, reducing Polish companies to mere subcontractors. As a consequence, Warsaw would prefer to develop its defense manufacture independently.
PORTUGAL

What does the province fear?
Portugal is ane of ii European Union countries that sees economical instability – which it associates with corruption, poverty, as well as social exclusion – as ane of the greatest threats to its safety (the other is Greece). Lisbon also regards province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood as a meaning threat, partly due to Portugal’s proximity to due north Africa as well as seat on NATO’s European southern flank. Portuguese leaders perceive terrorism, cyber attacks, as well as the deterioration of the rules-based international monastic enjoin as major threats that volition remain of import throughout the adjacent decade.
Who does the province fear?
Like many southern European Union states, Portugal perceives international criminal organisations that engage inward drugs, arms, as well as people trafficking as ane of the most threatening actors it faces. The province also views jihadists as a meaning threat, especially given that it participates inward the coalition fighting against the Islamic State group. Portugal is ane of v European Union members that regard Russian Federation as posing no threat to their safety (the others are Greece, Cyprus, Italy, as well as Hungary). Portugal acknowledges that Europe neighbours ii regions inward crisis: the Middle East as well as due north Africa, as well as eastern Europe. However, for reasons of proximity, it prioritises measures to counter threatening actors to its south.
Essential safety partners
Largely responsible for Portugal becoming a founding fellow member of NATO, London is Lisbon’s essential safety partner inward Europe. Portuguese leaders are concerned that Brexit could weaken non only the European Union but also the transatlantic relationship. Lisbon’s other key European partners include Madrid, Paris, as well as Rome. The Portuguese as well as the Italians are both preoccupied with stability inward the Middle East as well as due north Africa – a business organisation that has led them to cooperate with each other inward formats such as MED7, EUROMARFOR, as well as the 5+5 Dialogue. Portugal also increasingly cooperates with the Netherlands on defense investment. Nonetheless, historically, Portugal’s most of import strategic partner has been the United States. Lisbon has consistently sided with the US inward disagreements betwixt NATO countries, including that over the 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq. Portugal believes that its resilience against safety threats largely stems from its NATO membership as well as strategic alliance with the US.
The European Union as a safety actor
Portugal sees itself as both a European as well as a transatlantic power. The province is a founding fellow member of the eurozone as well as the Schengen Area. There is widespread back upwards for both the European Union as well as NATO amid Portuguese leaders – despite the fact that the ii far-left parties working with the ruling socialists inward parliament receive got traditionally opposed the US, NATO, as well as European integration. The Portuguese regime signalled its view of NATO as the nub of collective defense inward Europe past times avoiding PESCO’s launch ceremony. Lisbon initially feared the maiden would compete with NATO, distract the European Union from to a greater extent than pressing issues such as the eurozone, as well as impairment European Union cohesion (by, for instance, allowing large countries to dominate little ones inward defense industrial cooperation). Nonetheless, Portugal eventually joined PESCO because it wanted to remain at the forefront of European integration, as well as because it believed the maiden could ameliorate the interoperability as well as readiness of fellow member states’ armed forces.
ROMANIA

Go dorsum to the listing of fellow member states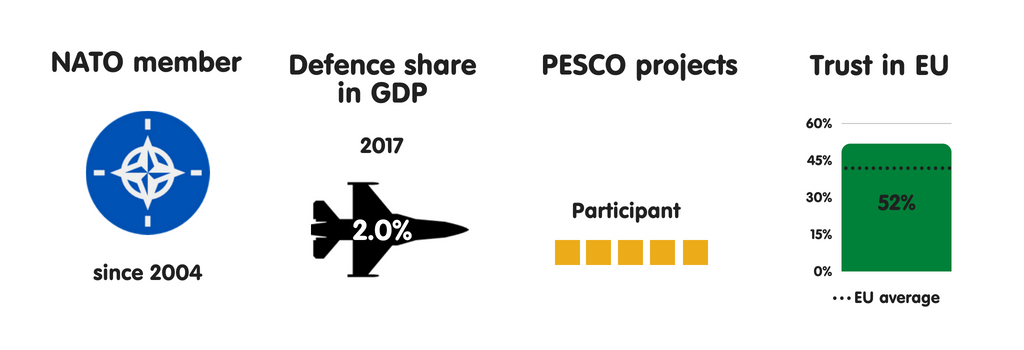 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear?
 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear? Romania perceives cyber attacks, province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, as well as inter-state state of war involving the province or its allies as beingness the greatest threats to its security. Romanians reckon their province as vulnerable due to its location inward a part of intense geopolitical contest betwixt the West as well as Russia. Romania’s 2013 conclusion to host parts of NATO’s missile-defence network (activated inward 2016) prompted heavy criticism from Moscow, which viewed the displace as designed to counter its nuclear arsenal.
Who does the province fear?
Romania’s regime as well as world view Moscow as past times far the most threatening instrumentalist they confront. As a consequence, Romania continuously seeks assurances as well as back upwards from the US as well as NATO inward protecting the alliance’s eastern flank, especially inward the Black Sea region. Romanaian perceptions of Russian Federation as a threat receive got intensified due to the country’s annexation of Crimea inward 2014, militarisation of the Black Sea, invasion of eastern Ukraine, as well as involvement inward a frozen conflict inward neighbouring Moldova. Bucharest is also concerned nigh the growing influence of Russian propaganda inward Romania through Sputnik as well as social media. There is a peril that Romania volition come upwards to reckon Republic of Hungary as a threat if the upcoming centenary of the Trianon Treaty reawakens historical enmity betwixt them.
Essential safety partners
Germany, France, as well as the UK are Romania’s key European safety partners due to their leading roles inward the European Union as well as NATO, as well as at the United Nations. However, Bucharest views Washington as easily its most of import safety ally. According to Romania’s National Defense Strategy 2015-2019, the country’s partnerships with the United States, NATO, as well as the European Union are the 3 pillars of its unusual policy – with NATO the main guarantor of Romanaian national security. This partnership with the US has led to, inter alia, naval deployments inward the Black Sea, a contract to provide Romania with F-16 fighter jets, as well as rotational US troop deployments inward Constanta. Determined to live a reliable partner for the US, Romania is ane of the few NATO members that spends at to the lowest degree 2 per centum of gross domestic product on defence.
The European Union as a safety actor
Romania heavily favours cooperation with Washington rather than the European Union as key to national security. The province remains sceptical of European safety guarantees due to its experiences inward the twentieth century. It is concerned that the force for European Union safety as well as defense cooperation could compete with NATO, endangering US involvement inward European security. Romania is ane of v European Union members to reckon some aspects of European Union membership as well as European integration as having both positive as well as negative effects on national safety (the others are Poland, Hungary, the Czech Republic, as well as Sweden). As a consequence, Romania has limited involvement inward PESCO. It joined PESCO to align with its key European partners – an especially of import business organisation given that it volition convey upwards the European Union presidency inward 2019 – as well as to ensure that the maiden complements NATO.
SLOVAKIA

Go dorsum to the listing of fellow member states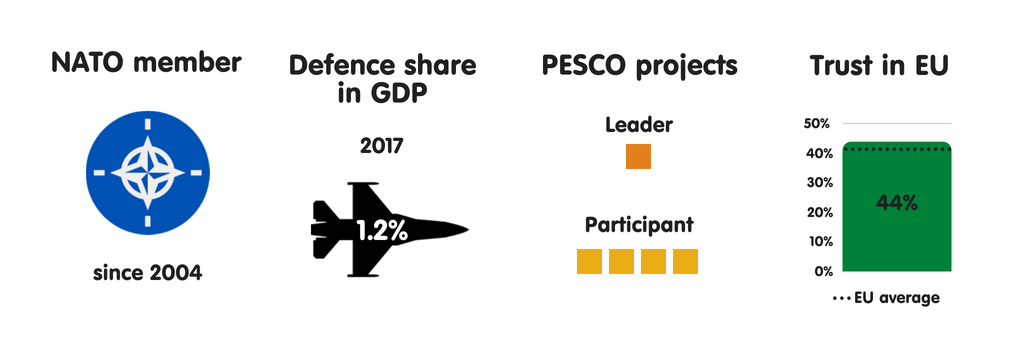 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear?
 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear? Slovakia views disruptions inward the unloose energy provide as well as province collapse or civil state of war inward the European Union’s neighbourhood as the most meaning threats to its security. Heavily reliant on Russian crude oil as well as gas, it is ane of 4 European Union countries that perceive such disruptions as at to the lowest degree a meaning safety threat (the others are Poland, Hungary, as well as Croatia). Bordering Ukraine, Slovakia feels exposed to instability inward the EU’s neighbourhood. Slovakia views external meddling inward domestic politics as a meaning threat, as well as is ane of 4 European Union countries that reckon fiscal issues as vital to national safety (the others are Greece, Portugal, as well as Malta).
Who does the province fear?
Bratislava views international criminal organisations as the most threatening actors it faces. Its perception of Moscow is to a greater extent than ambiguous. Unlike neighbouring Poland as well as the Czech Republic, Slovakia did non consider Russian Federation to live a threat until the annexation of Crimea inward 2014. The Security Strategy of the Slovak Republic 2017 casts Russian Federation inward a negative low-cal due to the country’s violation of international law as well as Ukraine’s sovereignty as well as territorial integrity. Although Slovakia’s ruling parties reckon Russian Federation as a valuable partner, most opposition groups – with the exception of the right-wing People’s Party Our Slovakia, which openly opposes the European Union as well as NATO – are at nowadays wary of Moscow.
Essential safety partners
Slovakia’s essential safety partners are the 3 other members of the Visegrád grouping (the Czech Republic, Poland, as well as Hungary). Bratislava closely cooperates with these countries on European issues, ofttimes inward an travail to formulate a shared key European narrative on issues such as migration. Slovakia also regards FRG as an of import partner on safety issues, non to the lowest degree because of its economical leadership as well as its seat at the EU’s core. Slovak Prime Minister Peter Pellegrini made his get-go 3 official unusual visits to Prague, Warsaw, as well as Berlin. As a NATO member, Slovakia sees the the States as a crucial safety partner, mostly due to the Article 5 safety guarantee.
The European Union as a safety actor
Slovakia by as well as large sees the European Union as an economical cooperation project, with NATO the focus of the country’s safety as well as defense policy. However, Slovakia strongly supports PESCO, especially as the launch of the maiden coincided with Slovakia’s conclusion to modernise its armed forces as well as increment military machine spending to 2 per centum of gross domestic product past times 2024. Unlike Warsaw, Bratislava does non view PESCO competing with NATO but rather a complementary construction that could assist the province strengthen its military machine capabilities. Slovakia leads PESCO’s EuroArtillery project, as well as participates inward 4 other strands of the initiative.
SLOVENIA

Go dorsum to the listing of fellow member states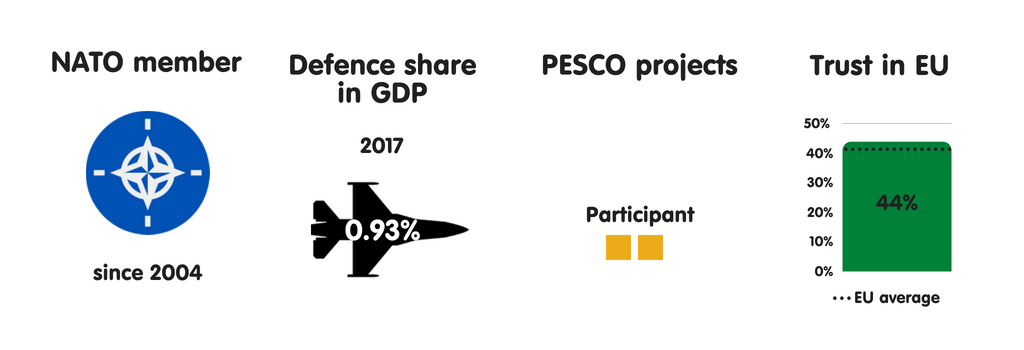 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear?
 What does the province fear?
What does the province fear? Slovenia expects uncontrolled migration to remain its greatest national safety business organisation for at to the lowest degree the adjacent decade. After Republic of Hungary closed its border with Serbia as well as Republic of Croatia inward 2015, Slovenia became the main entry signal for migrants travelling to the Schengen Area from the Western Balkans. In Oct 2015, around 12,500 migrants entered Slovenia – a province with 6,000 constabulary officers – per day. Since then, the Western Balkans route has closed (with Slovenia installing a razor wire fence on its southern border) as well as the European Union has reached an understanding with Turkey designed to command migration. Nonetheless, uncontrolled immigration into Slovenia is soundless creating domestic political tension. Ljubljana also fears instability inward the Western Balkans, due partly to political instability inward Kosovo as well as Macedonia, as well as partly to interference inward the part past times non-Western powers, especially Russia. Yet, confident inward the European Union as well as NATO, Slovene elites perceive in that location to live few major direct threats to their province that require an immediate response.
Who does the province fear?
Slovenia does non appear to view whatever ane instrumentalist as most threatening to its national security. Ljubljana is concerned nigh jihadists, but largely due to the transnational achieve of some terrorist organisations as well as Slovenia’s proximity to Western Balkans smuggling routes rather than the peril of attacks on Slovene territory. Slovenia also sees international criminal organisations as posing a moderate threat. It fears Russian Federation far less than most European Union countries do. Slovenia has supported the EU’s as well as NATO’s treatment of relations with Moscow since Russia’s military machine intervention inward Ukraine. However, Slovene leaders seek to maintain friendly political relations as well as strong economical links with Moscow.
Essential safety partners
Slovenia’s most of import European safety partners are other NATO members – especially French Republic as well as Germany, with which it has strategic partnership agreements. The Slovene Ministry of Defence sees Italy as a key partner inward NATO operations, as well as the UK as an of import partner due to its military machine capability as well as leading purpose within the alliance as well as at the UN. As a NATO member, Slovenia also sees the the States as an essential safety partner – mostly because of the US nuclear guarantee, but also because of Washington’s technological, military, as well as intelligence cooperation initiatives.
The European Union as a safety actor
Like their counterparts inward most other European Union countries, Slovene elites largely perceive the European Union as a transatlantic geopolitical projection that has NATO as its backbone – although they believe that the European Union could go a safety community. For now, the province sees NATO as its key safety guarantor as well as PESCO as primarily a mechanism for strengthening European military machine capabilities as well as peradventure developing shared European threat perceptions. Slovenia participates inward the ii PESCO projects it considers to live strategically important, partly with the intention of increasing its participation inward European Union operations.
SPAIN

What does the province fear?
Spain views cyber attacks as well as terrorism, followed past times uncontrolled migration as well as province collapse inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, as the most meaning threats to its national security. The province feels most vulnerable to cyber attacks. In contrast, inward 2008, the province felt most vulnerable to terrorism – having lately experienced Basque separatist as well as jihadist attacks – as well as to as well as so high levels of uncontrolled migration. Espana expects the threats it faces to persist at roughly their electrical current bird until at to the lowest degree 2028, with its business organisation nigh province collapse inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, European Union disintegration, as well as the deterioration of the rules-based international monastic enjoin growing during this period. Castilian leaders also anticipate turbulence inward due north Africa – with the probable ascent of novel leaderships inward People's Democratic Republic of Algeria as well as peradventure Kingdom of Morocco – inward the adjacent decade. Although Catalonia’s independence displace looms over its thinking on security, Espana views itself as resilient against external meddling inward domestic politics.
Who does the province fear?
Madrid perceives international criminal organisations as well as jihadists as the most threatening actors it confronts. The onetime receive got a meaning presence on the Mediterranean coast, as well as inward Cádiz as well as Galicia; the latter receive got carried out large-scale attacks inward Spain, including inward Madrid inward 2004 as well as inward Barcelona inward 2017. Russian Federation is the only province that Espana perceives as a moderate threat. Spain’s main political parties largely portion the safety establishment’s threat perceptions, albeit piece viewing Russian Federation as slightly less of a threat.
Essential safety partners
Spain sees France, Germany, Portugal, as well as Italy as its crucial safety partners within the EU. Madrid views Washington as its key ally inward NATO, recognising that the US troop presence at bases inward southern Espana are of import to the country’s powerfulness projection inward the Mediterranean. Most Spaniards receive got an extremely negative view of US President Donald Trump, but since the early 2000s the country’s human relationship with the US has go a less divisive political issue. There is strong bipartisan back upwards for the European Union as well as European defense as well as safety cooperation across Castilian political parties, especially the ruling Castilian Socialist Workers’ Party. Seeing Brexit as a potential source of safety problems, Madrid is keen for the European Union as well as the UK to rapidly create a novel safety partnership, thereby preventing whatever disruption inward intelligence as well as counter-terrorism cooperation. However, the safety establishment also views Brexit as an chance to pursue Spain’s claim to Gibraltar, as the European Union volition no longer live a neutral instrumentalist inward the Anglo-Spanish dispute over the territory.
The European Union as a safety actor
Maintaining a really positive mental attitude towards PESCO, Espana is determined to actively participate inward the initiative’s evolution as well as to live considered ane of the main drivers of European safety capabilities evolution as well as industrial cooperation. Madrid leads PESCO’s Strategic Command as well as Control System projection for European Union operations, seeing the evolution of capacity for military machine intervention as crucial to European Union security. The Rota naval base of operations inward Cádiz volition live ane of the EU’s v operational headquarters, replacing ane at Northwood after Brexit. The Rota base of operations volition also convey over from Northwood as the headquarters of Operation Atalanta. Espana supports the creation of the European Defence Fund within the adjacent European Union budget.
SWEDEN

What does the province fear?
Sweden views the deterioration of the rules-based international monastic enjoin as the greatest threat to its security, piece also perceiving cyber attacks as well as external meddling inward domestic politics as creating meaning risks. Stockholm views all these threats as having grown inward the past times decade – especially the deterioration of the rules-based international order, which it was non concerned nigh inward 2008. Sweden expects that, past times 2028, its greatest concerns volition live cyber attacks as well as the deterioration of the order. In low-cal of this, in that location is some debate inward Sweden nigh whether its strategic posture is appropriate to the electrical current safety environment. Sweden abandoned military machine service inward 2009, before partially reinstating it inward 2015. Sweden feels vulnerable to a make of threats, especially cyber attacks, disruptions inward the unloose energy supply, as well as military machine attacks on its territory. The province believes itself most resilient against economical instability.
Who does the province fear?
Sweden perceives Russia, followed past times jihadists, as the most threatening actors it faces. The number of whether joining NATO would mitigate these threats divides Sweden’s political parties. All of them worry that Moscow volition exploit European Union vulnerabilities to cyber attacks, information warfare, as well as diplomatic division. But they differ inward their conclusions on how NATO membership would impact European security. While the centre-right opposition wants to bring together NATO, the ruling Social Democrats as well as Green Party, along with the Left Party as well as the Sweden Democrats, oppose the move.
Essential safety partners
Sweden’s 4 key safety partners within the European Union are Finland, Germany, Denmark, as well as the United Kingdom. Sweden shares Finland’s threat perceptions on Moscow, as well as engages inward closed safety cooperation with the country; has a similar strategic civilization to Germany, with which it lately signed a missive of the alphabet of intent on increasing safety cooperation; shares Denmark’s threat perceptions on issues such as cyber attacks as well as hybrid warfare; as well as engages inward extensive intelligence cooperation with the UK, having lately joined the country’s Joint Expeditionary Force. Stockholm believes that Brexit could receive got negative safety implications, but could also ameliorate European Union safety as well as defense cooperation. Sweden also sees the the States as a vital safety partner, as well as sees increased investment inward defense capacity as an of import way to strengthen the countries’ relationship. Sweden is an active contributor to NATO-led missions, such as those inward the Balkans, Afghanistan, as well as Libya.
The European Union as a safety actor
As Sweden is non a fellow member of NATO, the European Union’s Article 42.7 on collective defense is especially of import to the country. Stockholm fully supports efforts to increment the EU’s safety as well as defense capacity, especially inward civilian crisis management. Sweden primarily joined PESCO to forbid the maiden from becoming exclusive as well as potentially divisive for fellow member states. It sees PESCO as potentially filling major gaps inward European defense capacity, but non as revolutionary for European Union safety as well as defense cooperation. Sweden’s limited participation inward PESCO comes at a depression cost.
UNITED KINGDOM

What does the province fear?
Like France, the UK perceives cyber attacks as well as terrorism as the most meaning threats to its security, but is also concerned nigh the deterioration of the rules-based international order, inter-state state of war involving the province or allies, province collapse inward the European Union’s neighbourhood, as well as climate change. The UK’s business organisation nigh economical instability has declined since 2008, piece its fright of cyber attacks has risen inward the period. London expects the threat from cyber attacks to persist at roughly its electrical current bird during the adjacent decade. The UK views itself as resilient against most threats, but vulnerable to that from some other global economical crisis (given the City of London’s prominent purpose inward global fiscal markets) as well as from external meddling inward its domestic politics (particularly inward relation to its 2016 vote on leaving the EU).
Who does the province fear?
The UK views jihadists as well as Russian Federation as the most threatening actors it confronts. The onetime receive got conducted attacks inward London as well as Manchester inward recent years, piece the latter is linked to the utilisation of nervus agent inward Salisbury inward March 2018. Having viewed Russian Federation as a relatively shaver threat inward 2008, UK policymakers are at nowadays to a greater extent than concerned nigh the province than nigh whatever other instrumentalist due its aggressive posture inward Europe – especially its annexation of Crimea; back upwards for political forces that undermine the dominion of law inward Europe as well as oppose the EU; disinformation campaigns; build-up of forces inward Kaliningrad, the Arctic, as well as the due north Atlantic; as well as increased military machine exercises on NATO’s borders. London also sees North Korea, Iran, as well as international criminal organisations as posing a meaning threat. The UK believes that the threat from Islamic Republic of Iran has declined since the implementation of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, as well as – assuming the bargain holds together inward some grade – volition receive got diminished farther past times 2028.
Essential safety partners
The UK perceives France, Germany, the Netherlands, as well as all Scandinavian countries as its key safety partners inward the EU. Intelligence sharing is key to all these relationships, with Franco-British cooperation also including technological collaboration as well as articulation training. London views Dublin as of import to internal safety due to their shared border. The UK is heavily invested inward its human relationship with the United States. Political coordination betwixt London as well as Washington, as well as the presence of American forces on British territory, receive got contributed to the UK’s security. But the focus of their safety human relationship is intelligence sharing (through the Five Eyes), technological central (covering back upwards for the UK’s nuclear deterrent as well as fifth-generation combat aircraft capability), as well as the US nuclear guarantee, nether Article 5 of the NATO Treaty.
The European Union as a safety actor
Although it has non joined PESCO, the UK views the maiden as potentially addressing NATO’s vulnerability to threats such as disinformation campaigns. Most British leaders recognise that farther European Union defense integration could contribute to the stability of the European projection as well as reckon a strong European Union inward their interests. However, the UK would live concerned nigh PESCO if the maiden began to compete with NATO. The UK hopes to live able to bring together some parts of PESCO after leaving the European Union (it remains unclear whether this 3rd province involvement volition live possible). London is especially keen to ensure that its departure from the Union volition non disrupt cooperation with the European Union on counter-terrorism, cyber security, as well as defense industrial development.
Buat lebih berguna, kongsi: