 At the start of 2018 ix states—the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, State of Israel in addition to the Democratic People’s South Korea (North Korea) — possessed but about 14,465 nuclear weapons.
At the start of 2018 ix states—the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, State of Israel in addition to the Democratic People’s South Korea (North Korea) — possessed but about 14,465 nuclear weapons. This marked a decrease from the but about 14,935 nuclear weapons that SIPRI estimated these states possessed at the get-go of 2017.
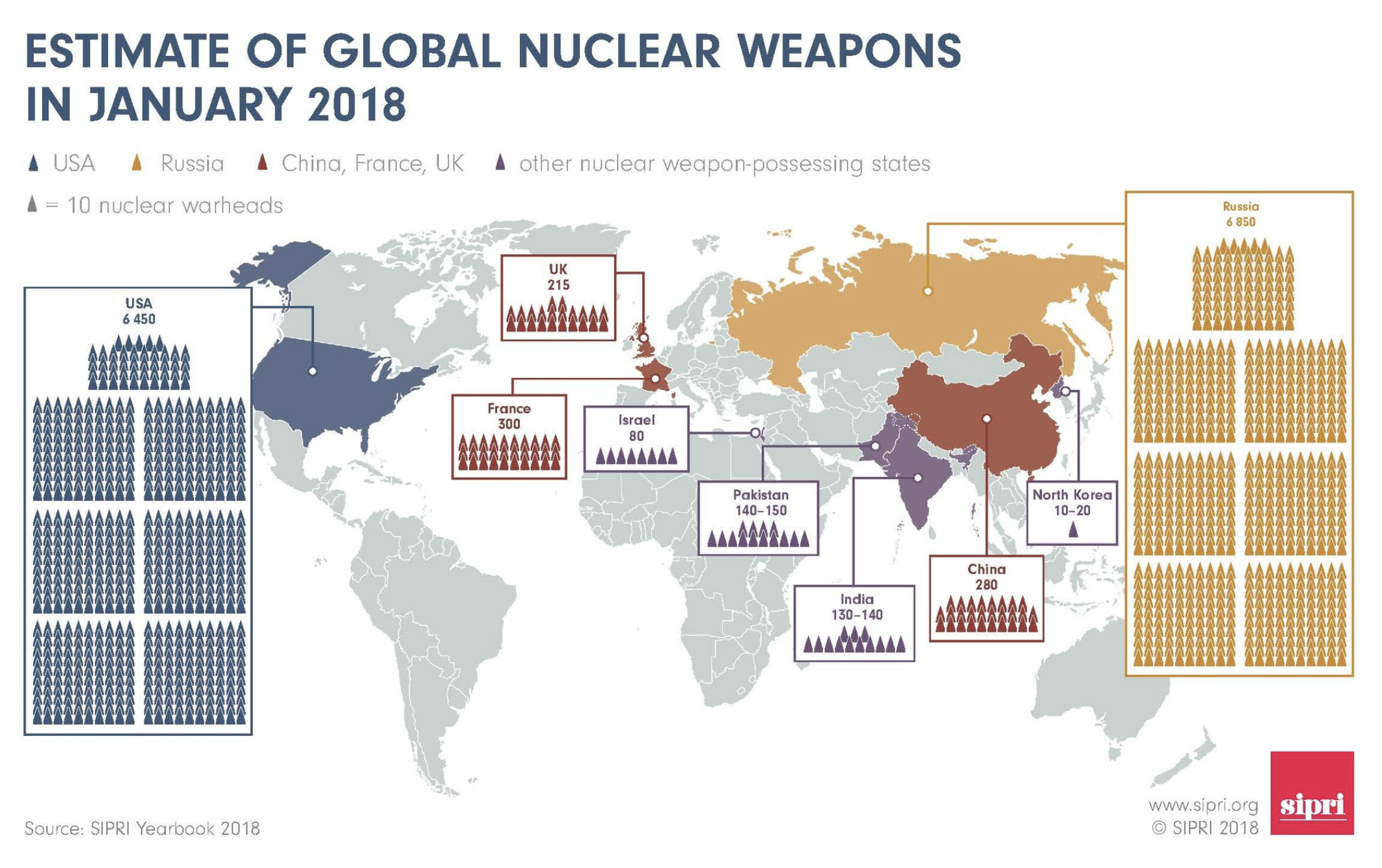
The decrease inwards the overall issue of nuclear weapons inwards the basis is due mainly to Russian Federation in addition to the US — which together however trouble organization human relationship for nearly 92% of all nuclear weapons — farther reducing their strategic nuclear forces pursuant to the implementation of the 2010 Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction in addition to Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START).
Despite making express reductions to their nuclear forces, both Russian Federation in addition to the US bring long-term programmes nether agency to supervene upon in addition to modernize their nuclear warheads, missile in addition to aircraft delivery systems, in addition to nuclear weapon production facilities.

The USA’s almost recent Nuclear Posture Review (NPR), published inwards Feb 2018, reaffirmed the modernization programmes in addition to approved the evolution of novel nuclear weapons.
The NPR likewise emphasized expanding nuclear options to deter and, if necessary, defeat both nuclear in addition to ‘non-nuclear strategic attacks’.
“The renewed focus on the strategic importance of nuclear deterrence in addition to capacity is a real worrying trend,’ says Ambassador January Eliasson, Chair of the SIPRI Governing Board. ‘The basis needs a clear commitment from the nuclear weapon states to an effective, legally binding procedure towards nuclear disarmament.

The nuclear arsenals of the other nuclear-armed states are considerably smaller, but all are either developing or deploying novel nuclear weapon systems or bring announced their intention to create so.
India in addition to Islamic Republic of Pakistan are both expanding their nuclear weapon stockpiles equally good equally developing novel land-, sea- in addition to air-based missile delivery systems. Communist People's Republic of China continues to modernize its nuclear weapon delivery systems in addition to is slow increasing the size of its nuclear arsenal.
In 2017 Democratic People's South Korea continued to brand technical progress inwards developing its nuclear weapon capabilities, including the examination of—what was claimed to be—a thermonuclear weapon, inwards September. Democratic People's South Korea likewise demonstrated unexpected rapid progress inwards the testing of 2 novel types of long-range ballistic missile delivery systems.
“Despite the clear international involvement inwards nuclear disarmament reflected inwards the determination inwards 2017 of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, the modernization programmes nether agency inwards the nuclear weapon-possessing states dot that genuine progress towards nuclear disarmament volition rest a distant goal,” says Shannon Kile, Senior Researcher amongst the SIPRI Disarmament, Arms Control in addition to Non-proliferation Programme.
The SIPRI Yearbook 2018 assesses the electrical flow terra firma of armaments, disarmament in addition to international security.
Buat lebih berguna, kongsi:
